| Citation: | Min Li, Yilamujiang Tuohetahong, Feng Lin, Rong Dong, Huaqiang Wang, Xiaoman Wu, Xinping Ye, Xiaoping Yu. 2022: Factors affecting post-release survival and dispersal of reintroduced Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon) in Tongchuan City, China. Avian Research, 13(1): 100054. DOI: 10.1016/j.avrs.2022.100054 |
Reintroduction has become a common conservation management tool to restore endangered species in their historical range. However, many attempts have failed to establish self-sustaining populations in the wild. The success of reintroductions could be improved by varying release strategies. Therefore, it is vital to determine the factors influencing reintroduction outcomes. To better understand the post-release settlement and to optimize the release strategy of the Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon), we quantified the effects of age, sex, acclimation duration, and the timing of release events on post-release survival and dispersal distance for the released Crested Ibis in Tongchuan City, Shaanxi Province, using a generalized linear mixed effect modeling approach. Our results indicate that 40–56.3% of the released individuals survived the first year following release. Mortality was attributable to flight collisions, starvation, disease, and unknown reasons. The post-release survival probability of ibises showed a negative association with age (estimate = −0.186; 95% CI: −0.350 to −0.022; P = 0.026), and post-release dispersal distance was affected by the timing of release event (estimate = 0.718; 95% CI: 0.025 to 1.253; P = 0.042). However, sex and acclimation period duration did not cause detectable differences in post-release survival probability and dispersal distance. Based on our results, optimal release strategies for establishing a reintroduced population of the Crested Ibis include: (1) release of sub-adults biased and sex ratio balanced initial groups; (2) release during the non-breeding season; and (3) food supplementation immediately after release.
With the aim of reducing the risk of extinction and enhancing genetic diversity of small animal populations, reintroduction is commonly used as a conservation management tool for endangered species (Seddon et al., 2007; Sheean et al., 2012). Many reintroductions have been implemented over the past two decades, including mammals, birds, fish, and reptiles (Seddon et al., 2005; Berger-Tal et al., 2020). However, approximately one-third of reintroduction efforts have been reported as unsuccessful and reintroduction success has not increased much over time (Griffith et al., 1989; Jule et al., 2008; Bubac et al., 2019). Moreover, reintroductions are typically expensive and labor-intensive undertakings, involving the restoration of release habitats, transfer of animals, pre-release acclimation training, and the provision of supportive measures (Miller et al., 1999). Thus, it is vital to establish which factors influence the success of reintroductions and to gain a broader understanding of the process of population establishment after release (Armstrong and Seddon, 2008; Taylor et al., 2017).
Reintroductions are generally considered successful if they result in self-sustaining populations (Fischer and Lindenmayer, 2000). However, it may take a long time to assess whether a population is viable in the wild (e.g., Millsap et al., 1998; Nelson et al., 2002). Released individuals typically show high mortality due to stress (Calenge et al., 2005), disease (Viggers et al., 1993; Joseph and Knapp, 2018), low-quality habitats (Moorhouse et al., 2009), and inexperience (Armstrong et al., 1999). Similarly, dispersal away from the release site, normally caused by stress response, homing behavior, and habitat selection, also has a significant impact on both individual fitness (e.g., body condition, the timing of breeding, clutch size) and population structure (Tweed et al., 2003; Dickens et al., 2010). Thus, short-term survival and dispersal are important parameters for evaluating the ability of released individuals to become established in their new environment.
The post-release population dynamics depend on a range of factors, including the source population of the released individuals (wild vs. captive-reared), the timing or season of release events, the size, sex ratio, and age structure of the released population, release methods (hard/immediate release or soft/delayed release) and post-release supportive management (e.g., supplementary food and predator control; Tweed et al., 2003; Armstrong and Seddon, 2008). Many case studies have attempted to identify important factors that contribute to reintroduction outcomes. For example, some studies have assessed the differences between captive-reared and wild-caught individuals by comparing the post-release survival of translocated individuals in similar circumstances (Sokos et al., 2008; Aaltonen et al., 2009; Roe et al., 2010). Tavecchia et al. (2009) proposed that late winter releases of Crested Coots (Fulica cristata) had higher survival than those released in summer. In terms of release methods, soft-release is widely advocated, as it is assumed this method can improve reintroduction success (Reading et al., 2013; Batson et al., 2015; Shier, 2016). However, the utility of soft-release is still debated (Mitchell et al., 2011; Batson et al., 2017; Bannister et al., 2020). The size, sex ratio, and age structure of the released population could also affect the probability of released individuals establishing in the target area (Bertolero et al., 2007; Pinter-Wollman et al., 2009; Imlay et al., 2010). Furthermore, Chauvenet et al. (2012) demonstrated that the benefits of supplemental feeding far outweigh the costs for the Hihi (Notiomystis cincta) population on Kapiti Island.
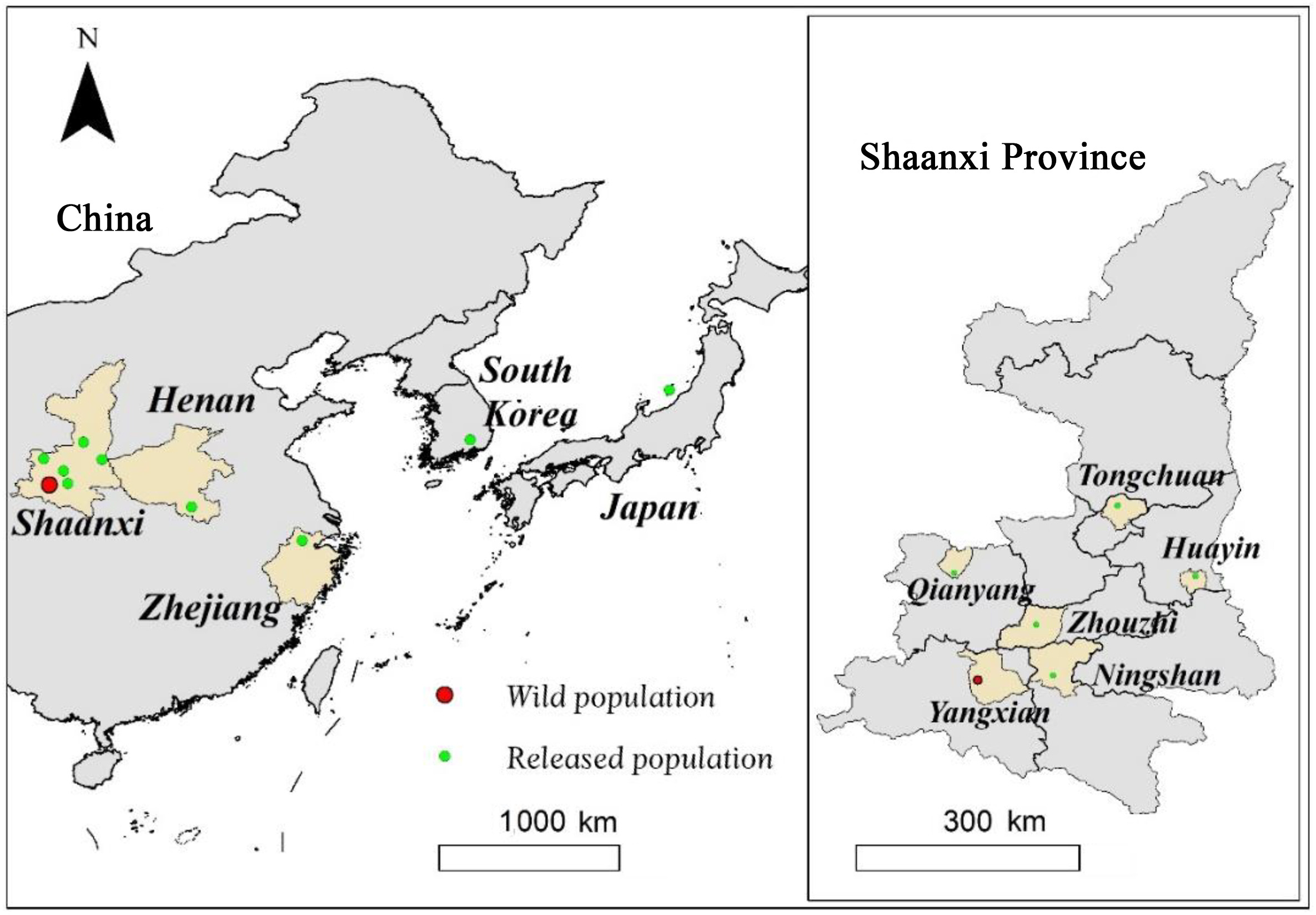
The Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon) is one of the most well-known endangered birds worldwide and is listed as Endangered in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (IUCN, 2021). In the 1980s, this species was considered to be almost extinct in the wild, mainly due to habitat alteration, hunting, disease, and pesticide abuse (Yasuda, 1983; Shi and Cao, 2001). Fortunately, the last wild population was rediscovered in Yangxian County, Shaanxi Province, China (Liu, 1981). To increase the population size and expand the distribution range of the Crested Ibis, a total of nine reintroduction projects have been carried out in different areas of China, including in Shaanxi (Yu et al., 2009, 2015, unpublished data; Wang, 2016; Li et al., 2020), Henan (Huang et al., 2016), and Zhejiang provinces (Qiu et al., 2020), as well as in Japan (Nagata and Yamagishi, 2016) and Korea (Yonhap News Agency, 2021; Fig. 1). Despite studies on survival rates (Li et al., 2018, 2020), breeding ecology (Yu et al., 2015; Dong et al., 2018), dispersal (Yu et al., 2010; Huo et al., 2014), post-release settlement (Nagata and Yamagishi, 2016), long-term sustainability (Wang et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2021) and habitat suitability (Wang et al., 2021) of reintroduced ibis populations, the factors affecting post-release establishment probabilities remain unclear, and few attempts have been made to evaluate and modify reintroduction protocols for this species.
To better understand the post-release settlement and to optimize the release strategy of the Crested Ibis, we intensively monitored the reintroduced ibis population in Tongchuan City, Shaanxi Province. Post-release survival and dispersal were examined to assess the short-term population dynamics of this reintroduction project. We also tested the effects of age, sex, acclimation period duration, and the timing of the release event on these two parameters. The findings from this study will provide valuable information for future reintroduction of the Crested Ibis and other endangered species.
The study area was located at Liulin Forestry Farm (35°04′77″ N, 108°82′19″ E), at the intersection of the Loess Plateau and the Guanzhong Plain, Yaozhou District, Tongchuan City, Shaanxi Province, China. This area lies in a warm, temperate zone with a continental monsoon climate. The mean annual rainfall is 554 mm and the mean annual temperature is 10.4 ℃. Released ibises use shallow streams, ponds, and wetlands around the Ju River for foraging. The vegetation condition of the release site was good, with dominant species including Chinese Pine (Pinus tabuliformis), False Acacia (Robinia pseudoacacia), Canadian Poplar (Populus × canadensis), and Chinese Scholar Tree (Styphnolobium japonicum), which were mostly used by ibises for roosting and nesting.
We sourced captive-bred birds from the Yangxian Crested Ibis Breeding Center (established in 1990, semi-free captive condition) and the Louguantai Crested Ibis Breeding Center (established in 2002, intensive captive condition) (Shi and Cao, 2001; Wang, 2016). Before transportation, each bird was quarantined by the veterinarian of the Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University (NWAFU). For pre-release acclimation training, all candidates were held together in a large circular nylon cage (20 m in height and 50 m in diameter; Fig. 2), containing roost trees and human-made foraging habitat to ensure that they were capable of flight, foraging, and socializing. The first release was conducted on 3 July 2013, with 32 birds (16 females and 16 males with an average age of 4.04 ± 0.63 years) kept in the enclosure for 13 days. For the second release, 14 birds (8 females and 6 males, kept in the enclosure for 39 days) and 16 birds (8 females and 8 males, kept in the enclosure for 111 days), with an average age of 10.23 ± 0.90 years, were released on 11 April 2015. Two release events were both designed as soft releases and supplementary food was provided during the first year after release as well as during food shortage in winter.
For post-release monitoring, all released birds were marked individually with numbered metal rings and colored plastic bands with alphanumeric codes (provided by the National Bird Banding Center of China) on their legs for identification in the field (Yu et al., 2010). Eight birds were fitted with lightweight radio transmitters (model AI–2B; frequency 138–235 MHz; battery life ~24 months; Holohil Systems Ltd., Carp, Ontario, Canada) and three GPS-GSM transmitters (model: HQBN3527; solar-powered; weight 27 g; Hunan Global Messenger Technology Co. Ltd., Hunan, China) were attached to Crested Ibis using a Teflon ribbon back harness. The survival status and locations of all released ibises were noted and monitored by radio receivers (TRX–1000S, Wildlife Materials Inc., USA), spotting scopes (GEOMA65A 20–60X), and binoculars (SICONG 10 × 42). On each tracking day, at least one location per individual was recorded during three periods: early morning (06:00–09:00), mid-day (09:01–15:00), and late afternoon (15:01–20:00). An individual was considered to have survived if it was re-sighted in the study area within one year after release (Wang et al., 2021). For the post-release dispersal distance, we excluded the individuals remaining within 1 km radius of the release site. Dispersal distance was measured as the Euclidean distance between the release site and the first nesting sites by using ArcGIS software (Version 10.8.1).
The survival probability of reintroduced Crested Ibis was considered binary (0/1), in which '1' represents survival and '0' means disappearance or death and we log-transformed the post-release dispersal distance to achieve normality. A binomial generalized linear mixed effects model (GLMM) with a logit link and a gaussian GLMM with an identity link were used to examine the effects of age, sex, acclimation duration, and release event timing (fixed factor) on post-release survival probability and dispersal distance, respectively, with individual and captive condition included as random effects (Breslow and Clayton, 1993). All statistical analyses were carried out using R (R Core Team, 2021). GLMMs were constructed with the package lme4 (Bates et al., 2016). Model selection statistics and statistical significance were calculated with package bruceR (Bao, 2020). The fixed factor coefficient estimates and 95% confidence intervals are listed in Table 1. In addition, the cause of mortalities were determined in terms of previous studies (Zhang et al., 2000; Li et al., 2013). We also commissioned the College of Veterinary Medicine, Northwest A & F University for the pathological identification of dead individuals. We report the mean ± SE (unless otherwise stated), and statistical tests were considered significant at P < 0.05.
| Variables | Estimate | SE | 95% CI | P-value |
| Survival probability | ||||
| Age | −0.186 | 0.084 | −0.350, −0.022 | 0.026* |
| Sex | −0.001 | 0.569 | −1.116, 1.114 | 0.999 |
| Duration | −0.012 | 0.012 | −0.036, 0.012 | 0.330 |
| Timing of release | 0.509 | 0.715 | −0.892, 1.911 | 0.476 |
| Dispersal distance | ||||
| Age | −0.018 | 0.022 | −0.575, 0.261 | 0.438 |
| Sex | −0.060 | 0.223 | −0.474, 0.367 | 0.719 |
| Duration | −0.001 | 0.004 | −0.603, 0.562 | 0.941 |
| Timing of release | 0.718 | 0.327 | 0.025, 1.253 | 0.042* |
| Significant results at probability < 0.05 are marked in bold. | ||||
From 2013 to 2015, a total of 62 captive-bred Crested Ibises were released in Yaozhou District, Tongchuan City. Of the 32 individuals in the first release, 11 females and 7 males (56.3%) survived in the wild, 2 females and 4 males (18.8%) were detected dead, and 8 individuals (25.0%; 3 ♀, 5 ♂) were considered to have disappeared since they were not re-sighted within the study area during the first year after release. Among the 30 ibises in the second release, 12 birds (40.0%; 5 ♀, 7 ♂) survived, 11 birds (36.7%; 6 ♀, 5 ♂) died, and 7 birds (23.3%; 4 ♀, 3 ♂) disappeared within the first year after release. We found that the post-release survival probability of released ibises showed a negative correlation with age (Fig. 3; estimate = −0.186, 95% CI: −0.350 to −0.022, P = 0.026). However, survival probability was not significantly related to sex, acclimation duration or the timing of release event (sex: estimate = −0.001, 95% CI: −1.116 to 1.114, P = 0.999; acclimation duration: estimate = −0.012, 95% CI: −0.036 to 0.012, P = 0.330; timing of release: estimate = 0.509, 95% CI: −0.892 to 1.911, P = 0.476; Table 1).
We tracked and monitored the post-release fate of the ibises and documented 17 mortalities (29.0%) in the first year after release (Table 2). In total, 35.2% of the released individuals (n = 6) died from unknown reasons. Disregarding these, the main causes of mortality included flight collisions (35.2%, n = 6), starvation (23.5%, n = 4) and Newcastle disease (5.8%, n = 1).
| Cause of death | Released in 2013 | Released in 2015 | Total | |||
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |||
| Flight collisions | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 6 | |
| Starvation | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Disease | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Unknown | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | |
| Total | 4 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 17 | |
Post-release dispersal distance of reintroduced ibis population were affected by the timing of release event (estimate = 0.718, 95% CI: 0.025 to 1.253, P = 0.042), with the mean dispersal distance of 6.67 ± 3.05 km (n = 10, range 1.02–31.49 km) for the first release, and 14.76 ± 2.33 km (n = 12, range 5.94–31.49 km) for the second release (Fig. 4). The mean dispersal distance for males and females were 9.69 ± 1.69 km (n = 11) and 12.48 ± 3.75 km (n = 11), respectively. Females dispersed farther than males, but these differences were not significant (estimate = −0.060, 95% CI: −0.474 to 0.367, P = 0.719). Furthermore, dispersal distance did not vary with the age of the released birds or acclimation duration (age: estimate = −0.018, 95% CI: −0.575 to 0.261, P = 0.438; acclimation duration: estimate = −0.001, 95% CI: −0.603 to 0.562, P = 0.941).
Low post-release survival probability and high rates of dispersal away from the release site can both reduce the size of the initial population and alter the composition of the founder group, ultimately influencing reintroduction outcomes (Seddon et al., 2012). Evaluation of alternative release strategies enables the formation of effective conservation measures to increase the success of species reintroductions (Wolf et al., 1996; Seddon et al., 2007). Although the reintroduction of Crested Ibis in Tongchuan City was not originally designed as a formal experiment to evaluate the efficacy of different release strategies, we note that several release-related variables correlated with population dynamics which could provide useful information for improving reintroductions of the Crested Ibis and other endangered species.
In general, juveniles in many reintroduced animals are expected to suffer higher mortality and disperse further than adults mostly due to inexperience and behavioral differences. However, the relationship between age and post-release population dynamics might be species-specific (Larkin et al., 2004). For example, adults of Saddlebacks (Philesturnus carunculatus) exhibit a greater tendency to die and disperse during translocations in New Zealand (Masuda and Jamieson, 2012). In the present study, the post-release survival of reintroduced Crested Ibis in Tongchuan City was age-specific: the survival probability of juveniles was significantly higher than that of older birds measured over the first year after release, but dispersal distance was not age-dependent in the focal population. Similarly, Wang et al. (2021) reported that the reintroduced ibis populations in Ningshan and Qianyang Counties showed higher survival probability in sub-adults compared to adults. It is possible that long-term captivity of adults results in low adaptation capabilities to new environments (Tenhumberg et al., 2004). Given that one of the criteria of reintroduction success is the production of a wild-born generation as soon as possible, Sarrazin and Legendre (2000) proposed that it is more efficient to release adults than juveniles by modeling the demographic consequences of releasing adult versus juvenile animals on reintroduction success. From this point of view, releasing a higher proportion of subadults (juveniles and yearlings) could lead to delayed population growth because of the 2-year sexual maturation period of Crested Ibis (Ding, 2004).
Post-release pressures could differ between the sexes and lead to skewed mortality or dispersal in monogamous species (Gowaty, 1993; Bradshaw et al., 2003; Kapota et al., 2016). Consistent with the movement pattern observed for the reintroduced Crested Ibis population on Sado Island in Japan (Nagata and Yamagishi, 2016), females disperse over greater distances than males in Tongchuan City, but these differences were not statistically significant (Table 2). Green et al. (1996) showed that released White-tailed Sea Eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla) failed to form pairs in Scotland because of chance differences in the numbers of males and females. Therefore, an initial balanced sex ratio might be crucial to maximize the population growth rate for reintroductions.
Soft-release typically involves temporarily confining animals in enclosures containing food, water, shelter, and providing supplementary food after release (Cid et al., 2014). Several studies show that soft-release reduces dispersal, increases site fidelity, and improves survival because candidates could recover from capture and transportation, and then acclimatize to new habitats and develop social relationships sooner (Bright and Morris, 1994; Tuberville et al., 2005; Mitchell et al., 2011; Knox and Monks, 2014). However, soft-release could increase the risk of injury and stress, as well as reduce the survivability in the wild (Thompson et al., 2001; Richardson et al., 2015; Batson et al., 2017; Bannister et al., 2020). For the reintroduced Crested Ibis in Japan, a soft-release strategy encouraged birds to form flocks shortly after release and increased site fidelity (Nagata and Yamagishi, 2016).
Pre-release acclimation is a common soft-release technique, especially in birds (Wanless et al., 2002), but few studies have tested the effect of holding period length. On average, acclimation training was recognized as resulting in a suite potential benefits that lead to higher survival rates (Brown and Day, 2002; Wanless et al., 2002). For example, Liu et al. (2016) found that the survival rate for the reintroduced Cabot's Tragopan (Tragopan caboti) in Hunan Province was significantly improved by the length of time spent in the soft-release enclosure. For the reintroduced ibises in Tongchuan, 11 (56.3%), 7 (50.0%; 4 ♀, 3 ♂), and 5 (31.3%; 1 ♀, 4 ♂) birds survived during the first year after release following 13, 39, and 111 days of acclimation training, respectively. However, the variation in survival among groups of ibises with different acclimation period duration was not statistically significant. Moreover, we did not detect a difference in post-release dispersal distance between groups of ibises with different acclimation period durations, although dispersal distance decreased with increasing acclimation duration for the second released birds (39 days: 16.07 ± 3.95 km; 111 days: 12.92 ± 1.20 km).
Timing of release events should be considered in conjunction with species-specific life history traits (e.g., migration or reproduction) of the animals during the planning of any reintroductions. For instance, Le Gouar et al. (2008) suggested that releasing animals before the breeding period is more appropriate because they are less liable to move. Our study showed that the ibises released during the breeding period dispersed over greater distances than those released in the non-breeding seasons. In addition, trade-offs between dispersal and reproduction are known to be important drivers of population dynamics (Hughes et al., 2003; Kendrick et al., 2017). Among the Crested Ibis released in 2013, 2 pairs formed and 2 nestlings fledged successfully during the first breeding season after release (Wang, 2016). However, the second group of reintroduced ibises did not breed in the year of release or during the following year. The process of translocating seems to decrease the reproduction of individuals through a variety of physiological, ecological, and behavioral mechanisms. Firstly, the post-release survival-related exploratory movements became a priority for the released ibises. Secondly, the short-term reproductive performance may be reduced by the stress response of confinement and release individually or interactively. Finally, in case of food shortage during the non-breeding season, released birds may benefit from the provision of supplementary food.
In conclusion, the following protection measures are proposed based on our results: (1) release of sub-adult biased and sex ratio balanced founder groups is vital to increase the survival probability of reintroduced ibises; (2) release in the non-breeding period and food supplementation immediately after release could reduce post-release dispersal. Long-term post-release monitoring is important and necessary to evaluate reintroduction success (Mitchell et al., 2011; Sheean et al., 2012). However, this study focused on the factors influencing the short-term establishment of the reintroduced Crested Ibis and did not measure the long-term persistence of the population. Additionally, other factors, such as captive conditions, pairing history, or the presence of previously released animals, may have impacts on the establishment of reintroductions (Seddon et al., 2012). Therefore, we suggest that more efforts need to be made for reintroductions in future research.
ML and X. Yu conceived and designed the study. ML, FL, RD, HW, and XW conducted the fieldwork. ML and YT carried out the analyses. ML prepared the draft of the manuscript and X. Yu and X. Ye revised it. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
We thank the staff of Yaozhou District Wildlife Protection and Management Station in Tongchuan City for providing logistical help and research aid. Special thanks to Dr. D.R. Gustafsson for his English improvement. The study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31572282, 31872245) and Shaanxi Forestry Bureau.
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avrs.2022.100054.
|
Breslow, N.E., Clayton, D.G., 1993. Approximate inference in generalized linear mixed models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 88, 9-25.
|
|
Ding, C., 2004. Research on the Crested Ibis. Shanghai Scientific and Technological Education Publishing House, Shanghai.
|
|
Huang, Z., Wang, K., Cai, D., Zhu, W., Pan, X., Liu, D., 2016. Acclimation of captive Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon) before reintroduction in Dongzhai of Henan Province. Chinese J. Ecol. 35, 3017-3022.
|
|
Joseph, M.B., Knapp, R.A., 2018. Disease and climate effects on individuals drive post-reintroduction population dynamics of an endangered amphibian. Ecosphere 9, e02499.
|
|
Li, M., Ye, X., Dong, R., Zhang, X., Zhang, H., Yu, X., 2020. Survival rates and reproductive ecology of a reintroduced population of the Asian Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon) in Shaanxi Qianhu National Wetland Park, China. Bird Conserv. Int. 31, 410-419.
|
|
Li, X., Huo, Z., Yu, X., 2013. Mortality and cause of death of the Crested Ibis of a reintroduced population in Ningshan, Shaanxi. Chinese J. Zool. 48, 701-706.
|
|
Liu, Y., 1981. The re-discovery of the Crested Ibis in Qinling Mountain. Acta Zool. Sinica. 27, 273.
|
|
Masuda, B.M., Jamieson, I.G., 2012. Age-specific differences in settlement rates of saddlebacks (Philesturnus carunculatus) reintroduced to a fenced mainland sanctuary. New. Zeal. J. Ecol. 36, 123-130.
|
|
Millsap, B.A., Kennedy, P.L., Byrd, M.A., Court, G., Enderson, J.H., Rosenfield, R.N., 1998. Review of the proposal to de-list the American peregrine falcon. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 26, 522-538.
|
|
Qiu, G., Fu, C., Zhang, R., Wan, Q., Fang, S., 2020. Behavioral differences between captive and reintroduced populations of Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon). Chinese J. Wildl. 41, 376-386.
|
|
Seddon, P.J., Strauss, W.M., Innes, J., 2012. Animal translocations: what are they and why do we do them. In: Ewem, J.G., Armstrong, D.P., Parker, K.A. (Eds.), Reintroduction Biology: Integrating Science and Management. Wiley-Blackwell, West Sussex, UK, pp. 1–24.
|
|
Shi, D., Cao, Y., 2001. The Chinese Crested Ibis. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing.
|
|
Shier, D.M., 2016. Manipulating animal behavior to ensure reintroduction success. In: Berger-Tal, O., Saltz, D. (Eds.), Conservation Behavior: Applying Behavioral Ecology to Wildlife Conservation and Management. Cambridge University Press, UK, pp. 275–304.
|
|
Wang, H., 2016. Reproduction of reintroduced Nipponia nippon in Tongchuan, Shaanxi Province. Sichuan J. Zool. 35, 471-474.
|
|
Yasuda, K., 1983. Distribution of Crested Ibis as Found in Literature. Newton Books: Nipponia nippon, Tokyo.
|
|
Yu, X., Chang, X., Li, X., Chen, W., Shi, L., 2009. Return of the Crested Ibis Nipponia nippon: a reintroduction programme in Shaanxi Province, China. Birding ASIA 11, 80-82.
|
|
Zhang, Y., Lu, B., Zhai, T., Xi, Y., Wang, Y., 2000. Analysis on the death reason and conservation measures of Crested Ibis. In: Proceedings of International Workshop on the Crested Ibis Conservation’99. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing, pp. 117–122.
|
| Variables | Estimate | SE | 95% CI | P-value |
| Survival probability | ||||
| Age | −0.186 | 0.084 | −0.350, −0.022 | 0.026* |
| Sex | −0.001 | 0.569 | −1.116, 1.114 | 0.999 |
| Duration | −0.012 | 0.012 | −0.036, 0.012 | 0.330 |
| Timing of release | 0.509 | 0.715 | −0.892, 1.911 | 0.476 |
| Dispersal distance | ||||
| Age | −0.018 | 0.022 | −0.575, 0.261 | 0.438 |
| Sex | −0.060 | 0.223 | −0.474, 0.367 | 0.719 |
| Duration | −0.001 | 0.004 | −0.603, 0.562 | 0.941 |
| Timing of release | 0.718 | 0.327 | 0.025, 1.253 | 0.042* |
| Significant results at probability < 0.05 are marked in bold. | ||||
| Cause of death | Released in 2013 | Released in 2015 | Total | |||
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |||
| Flight collisions | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 6 | |
| Starvation | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Disease | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Unknown | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | |
| Total | 4 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 17 | |