| Citation: | Shilong Liu, Qiao Xie, Aiwu Jiang, Eben Goodale. 2022: Investigating how different classes of nest predators respond to the playback of the begging calls of nestling birds. Avian Research, 13(1): 100044. DOI: 10.1016/j.avrs.2022.100044 |
Begging brings benefits and costs for nestling birds: it can indicate their needs to their parents, but it can also be a cue used by predators to find the nest. The costs, like many variables related to nest predation, can be specific to what kinds of predators are present and their auditory capabilities. These costs and benefits could also be affected by human noise, as noise could disrupt communication to parents and eavesdropping by predators, although human-produced noise might be easily ignored if predators can hear high-frequency components of the begging. We studied nest predation on a generalist bird, the Red-whiskered Bulbul (Pycnonotus jocosus), in a tropical forest in which there are many kinds of nest predators, including birds, mammals and reptiles. In 20 natural nests in which artificial eggs were placed, and subsequently in 140 artificial nests, we broadcast recordings of begging nestlings, with and without traffic noise, at two volume levels. We hypothesized that playback would increase predation relative to a silent control, and that mixing in traffic noise with the begging would decrease predation, as the begging signal was masked. However, we hypothesized that some predators, particularly small mammals with sensitive high-frequency hearing, might ignore the traffic noise. We found that predation was lowest for the control treatment, and lower for treatments mixed with traffic noise than for those without it. Small mammals, however, showed an unexpected pattern, displaying less nest predation in the treatments with traffic noise. Our results demonstrate the human-associated noise can disturb nest predators and influence which kinds of predators use begging to locate nests.
Nest predation is a major cause of mortality for birds, and hence has strongly shaped their life histories (Ricklefs, 1969; Martin, 2015; Hu et al., 2020). Nest predation appears higher in tropical areas (Stutchbury and Morton, 2001; Brawn et al., 2011), and also in human-disturbed habitats (Chalfoun et al., 2002; Stephens et al., 2004; Vetter et al., 2013; Vincze et al., 2017). It is thus possible that anthropogenic change may lead to new predation threats for nestling birds and an overall threat to avian conservation (Ibáñez-Álamo et al., 2015). However, there is a great degree of variability among different habitats and regions in their dominant nest predators (DeGregorio et al., 2016), and different predators vary in how they detect nests (e.g., through vision, auditory or chemosensory cues) and how accessible nests are to them (Soanes et al., 2015). Therefore, most meta-analyses of nest predation have struggled to find general patterns (Chalfoun et al., 2002; Stephens et al., 2004; Vetter et al., 2013; Vincze et al., 2017).
The effect of nestling begging on nest predation is a theoretically interesting question because, although it helps parents understand the nutritional needs of their young, begging also provides a way for audio-sensitive nest predators to find nests (Magrath et al., 2010). Several playback experiments have shown that begging can increase exposure to nest predation (Haskell, 1994; McDonald et al., 2009; Haff and Magrath, 2011), and the addition of loudly-begging nestling cuckoos to nests also can increase predation (Ibáñez-Álamo et al., 2012a). Birds have evolved to minimize the attraction of begging calls to predators; for example, ground-nesting birds, which may suffer greater costs of begging (i.e., attracting more nest predators; Haskell, 1994), have higher frequency begging calls, which transmit less distance and hence are more difficult to detect (Haskell, 1999).
Given the importance of nest predation to birds, and begging to nest predation, a crucial question is how begging activity, and predator response to it, is impacted by human disturbance. General adaptations of bird vocalizations to human disturbance are well-known. For example, birds have been shown to increase the frequency of their vocalizations in noisy conditions (Slabbekoorn and Peet, 2003). Animals may also increase the volume of sounds in noisy conditions, which is called a Lombard effect (Brumm and Zollinger, 2011). Indeed, a study on begging nestlings showed that nestlings increased the volume of their begging in noisy conditions (ambient noise in the field, white noise in laboratory tests; Leonard and Horn, 2005). This research raises the question of whether it is possible that noise could make nestling birds particularly susceptible to predators. As human-made noise is generally at low frequencies (in most cases peaking below 1 kHz; Brumm and Zollinger, 2011; although there can be some high frequency components; Nemeth and Brumm, 2010) and begging can be at quite high frequencies (with considerable components above 6 kHz; Haskell, 1999), if nestling birds increase their begging volume under noisy conditions, nest predators that orient acoustically might detect more easily the increased volume at high frequencies where it is not masked. This detection would be dependent on high-frequency hearing that could vary among nest predators: large birds have been shown to have less sensitive hearing than passerines at the upper range of avian hearing (between 5 and 8 kHz; Klump et al., 1986), but small mammals like rodents routinely communicate in the ultrasonic (> 20 kHz; Portfors, 2007).
We performed a playback experiment to look at the attraction of predators to begging calls, and begging calls mixed with traffic noise, at a study site with a great variety of predators (birds, mammals, and reptiles). We hypothesized that: 1) treatments that had the playback of begging would attract more predation than a control treatment (silence); 2) playback at maximum volume (the highest amplitude of naturally recorded nestlings) would attract more predators than playback at mean volume; 3) playback with traffic noise mixed with begging calls would attract fewer predators, because the begging calls would be partially masked, especially at lower frequencies (< 6 kHz; see methods for descriptions of the exact frequencies involved). However, we predicted 4) that when begging calls mixed with noise were played at maximum volume, the increase in volume, especially at high frequencies (> 6 kHz) where the calls were unmasked, would attract nest predators that had particular sensitivity to high frequency sounds, such as small mammals.
The study was conducted in and around the Nonggang National Nature Reserve (22°28′–22°30′ N, 106°56′–106°58′ E; elevation 59–215 m a.s.l.), using the nests of the Red-whiskered Bulbul (Pycnonotus jocosus). Nonggang is a tropical limestone site, where researchers have spent a decade investigating the breeding ecology of the avifauna (Jiang et al., 2013). It is located in the southwest part of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, southern China and has a tropical monsoonal climate (Jiang et al., 2017). The Red-whiskered Bulbul is abundant in buffer areas of the reserve which includes degraded forest, as well as plantations of sugarcane and the Chinese Chestnut (Sterculia nobilis), and its nesting has previously been studied in this area (Jiang et al., 2015). Its breeding season lasts for about five months, from early April to late August, and we worked on this study throughout the breeding season, during three years, 2018–2020. Nest predation of Red-whiskered Bulbuls has been studied at another tropical site of Southwest China (Xishuangbanna, Yunnan), and been shown to involve a range of nest predators, including birds (coucals, magpies, owlets and Accipiter hawks), mammals (tree shrews, squirrels, mice, feral cats), and reptiles (primarily snakes; Li et al., 2019). Primates, such as Macaques (Macaca spp.) which can be major nest predators in Thailand, are very rare in the nesting habitat of Red-whiskered Bulbuls in Nonggang; the other nest predators described from Thailand are generally similar to those of Xishuangbanna (Pierce and Pobprasert, 2013; Chotprasertkoon et al., 2017; Khamcha et al., 2018; Somsiri et al., 2020). In this region, the majority (~2/3–7/8) of nest predation is diurnal (Pierce and Pobprasert, 2013; Khamcha et al., 2018; Li et al., 2019).
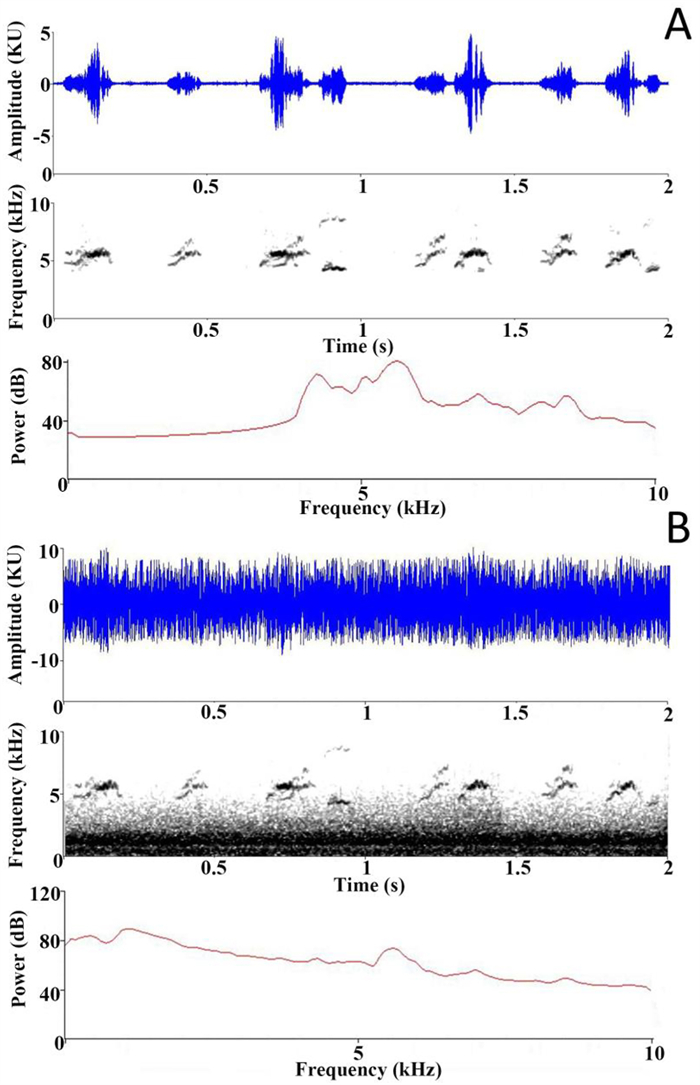
We recorded begging calls at six nests in the buffer zone of Nonggang during May of 2018. We checked nests every two days to document when the eggs hatched and hence the age of the nestlings. When nestlings were five days old and parents were not present at the nest, we positioned the end of a CR: 152B model Cirrus Research sound level meter (SLM) about 1 cm close to the beak of the nestlings. The nestlings responded to this stimulus by producing begging calls, as if in response to the parent (for similar behavior; see Moreno-Rueda, 2005). The SLM recorded 3 min of amplitude data, using its fast response setting and A weighting, with one data point collected every 1 s. The nestling calls' fundamental frequencies were between ~4.5 and 6 kHz, with considerable harmonics up to 7.5 kHz (Fig. 1).
At the same time as we recorded the amplitude of the vocalizations using the SLM, we also recorded those vocalizations using a K6 Sennheiser ME 62 omnidirectional microphone, placed 10 cm away from the nestlings, embedded in a Telinga parabola, and attached to a Marantz PMD 671 digital recorder. Recordings were made at 44,100 kHz sampling rate and in the.wav format. We then repeated this process when nestlings were seven days old. We took care not to overly disturb the nest, and the whole recording process at a nest lasted for only 10 min. Our manipulations did not appear to affect the success of the nests adversely, as four of six (66.7%) of the nests in which we worked fledged successfully, higher than the average success of nests in the area (nest success: 9/31 nests, 29.0%; Jiang et al., 2015).
In analyzing the SLM amplitude measurements, we found the difference between the amplitude when the chicks were begging (averaged across all such seconds), and the amplitude when the chicks were not begging (i.e., background noise), and calculated the amplitude of the begging (Brumm and Zollinger, 2011). We found no significant differences in amplitudes between the 5- and 7-day recordings. Pooling these two types of recordings together, we had 12 measurements of the amplitude of begging, averaging 73.1 ± 5.9 dB at 1 cm (hereafter referred to as "mean amplitude"). The loudest exemplar was 83.9 dB at 1 cm (hereafter referred to as "maximum amplitude").
We placed an FHD-480 model RICH video camera close to (~2–3 m away) from three nests to document typical parental behavior, over 24 h. Based on the data from the video cameras, we found the frequency of parental feeding was approximately 5–6 trips/h, with the earliest feeding about 6:00 a.m., and the latest about 6:00 p.m.
We selected traffic noise as the type of noise used in this study because it is perhaps the most pervasive kind of anthropogenic terrestrial noise. We recorded traffic noise at close range because at this distance we found the high-frequency components to be considerable, so that they provided masking towards the lower frequencies of the begging of the bulbuls (i.e., around 4.5 kHz; Fig. 1). If nestling birds perceive some interference from traffic noise and increase their begging volume, as the experiments of Leonard and Horn (2005) suggest they might, the higher frequency components of their vocalizations (e.g., 6 kHz and above) would not be as masked as their lowest frequencies (e.g., 4.5 kHz), and this might make them more vulnerable to predators that have sensitive high-frequency hearing.
We recorded traffic noise 5 m from large highways near Nanning, the capital city of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, using the same recording equipment as above, and with the microphone pointed into the flow of traffic. We made six separate recordings 3 km apart on the highway that circles Nanning on one day (8:00 a.m. to 12 p.m., March 20, 2018). Although the amplitude of the recordings was made so that it did not change over time, there were some fluctuations in the mix of frequencies (0–6 kHz) on the recordings: the amount of energy above 4.5 kHz could be as high as ~1/10 of the total energy as a car approached, and less than ~1/50 when the cars were departing or distant.
There were two kinds of playback treatments to prepare: begging tapes and the same begging sounds mixed with traffic noise. To make the begging tapes, we took the 1 min sections of the 3 min recordings with the greatest number of begging calls. Using Raven Pro (Version 1.5, Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology) we filtered the tapes (below 0.7 kHz), and edited them to remove background noises, while keeping the original repetition rate of the begging calls. To make the mixed tapes, we used Audacity (version 2.4.1, Audacity Team) to mix with any begging recording an equal amplitude of traffic noise, so that at peak amplitudes (i.e., when the chick called) the total amplitude of the mixed tape consisted of half begging and half traffic noise (as judged using the dimensionless units of amplitude (kU) in Raven Pro's waveform display, see Fig. 1). Begging was partially masked by the traffic noise, although the majority of the power of the traffic noise was at lower frequencies. The masking effect had some fluctuation according to the approach and departure of the cars, with an approximately average situation shown in Fig. 1.
Playback tapes were then made that were 12 h long, with a 1-min section of begging calls followed by 10 min of silence repeated many times to replicate the patterns that had been recorded by the videocameras. There was a total of five playback treatments: 1) begging played at mean volume (BEG); 2) begging played at maximum volume (BEGMAX); 3) mixed (begging calls + traffic noise) played at mean volume (the same volume as treatment 1, BEGNOISE); 4) mixed played at maximum volume (the same volume as treatment 2, BEGNOISEMAX); and 5) the silent control (SILENT). We made six playback exemplars, consisting of the recordings from the six nests, randomly combined, for some treatments, with the six noise recordings; a set of such exemplars was made for the 5-day recordings and a separate set for the 7-day recordings.
Small speakers (AM1 Plus Abramtek speaker, China, which have an approximately flat frequency response curve between 100 and 10000 Hz) were hung 3–10 cm from the nest. Volume was controlled by adjusting the volume of the speaker so that it matched the mean amplitude (begging and noise at ~77 dB, with noise at ~75 dB, producing an amplitude of begging at ~73 dB, all assessed at 1 cm from the speaker) or the maximum amplitude (begging and noise at ~88 dB, with noise at ~86 dB, producing an amplitude of begging at ~84 dB, again at 1 cm from the speaker) of the measurements of begging. Playback was started at 6 a.m. and played until 6 p.m. for seven straight days, with 5-day old nestling recordings used the first four days, and 7-day old nestling recordings used the last three days. On each day a playback exemplar (one of the six) was chosen randomly, as long as it had not been used at that nest before. In the SILENT treatment, the speaker was placed near the nest, but not turned on.
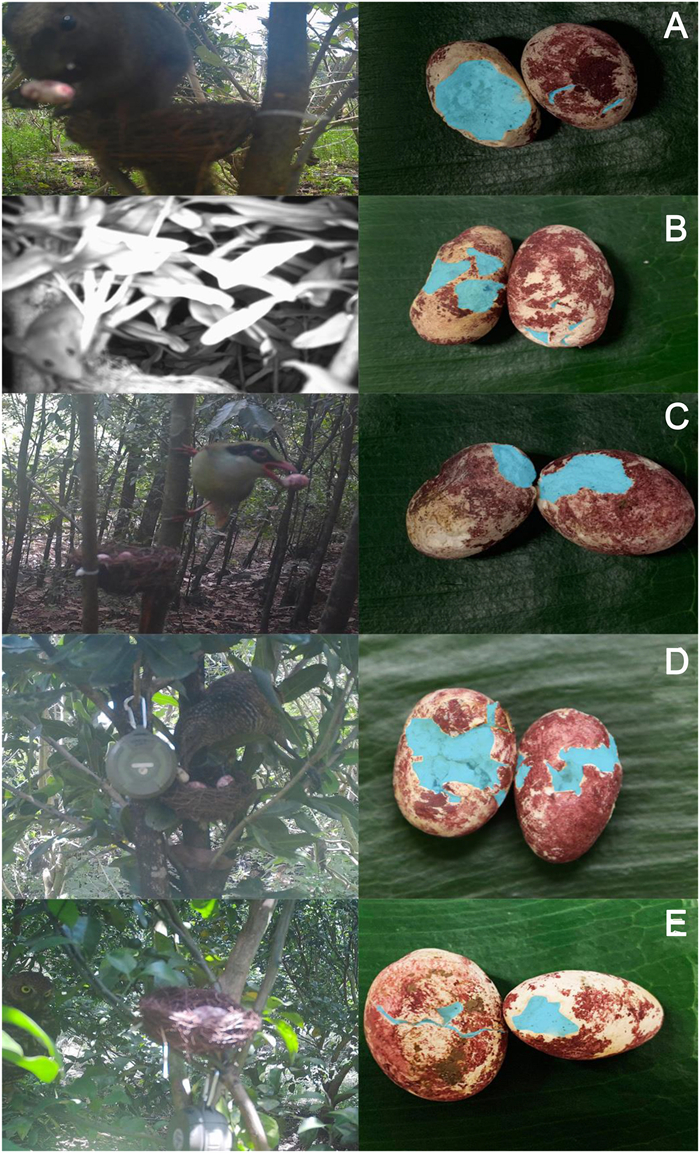
In the beginning of the project (the 2018 field season), we conducted the experiment at nests that had been used that year. After the nestlings fledged or were predated, we waited one week, and then reused the nest, provided they were not damaged. Wearing plastic gloves, we first cleaned the nests of any excrement or egg shells. We then placed eggs made of plasticine in the nests. These eggs were made to mimic Red-whiskered Bulbul eggs in their size (approximately 16 mm × 22 mm) and coloring (marks were painted on the plasticine using waterproof paints). In addition to the speaker, we also placed at the nest an infrared camera trap (SG-660v, Shenzhen Siyuan Digital Technology Co., China) to detect predation events. This camera was always positioned slightly higher than the nest so that the eggs were visible, and was kept 0.5–1.0 m away horizontally. We acknowledge that this camera trap can be insensitive to certain types of predators like snakes, or rapidly moving predators (Li et al., 2019); indeed, for 32 nests that were predated, we were unable to assign the predator.
A nest was considered to be predated if at least one egg was damaged or disappeared. Each nest was assigned to one treatment randomly, as long as nests with the same treatment were not within 250 m of each other. In 2018, we used 20 such nests. A problem with the natural nests was that they were frequently damaged by rainfall, limiting the number of nests in which we could put the artificial eggs. In order to increase the sample size, we used hand-made artificial nests, constructed out of dried twigs and vines to be of similar size and shape to the bulbuls' nests and painted to resemble them. In 2018, we installed 40 of these artificial nests in locations where we had observed actual nests over the previous two years (in other projects), but where these nests had been damaged. The overall predation rate, and the composition of the nest predators, was similar to that of the natural nests (see results). We therefore used artificial nests in the last two years of the study (2019 and 2020, 100 nests), again placing them at places where real nests had been located that year (the birds did not reuse the same locations year-after-year). As all nests were located where natural nests had been previously, the sites of the nests were selected by the birds. We did not make any efforts of our own to standardize the concealment of nests, which can influence the amount of nest predation and which predators find nests (Chotprasertkoon et al., 2017; Somsiri et al., 2020).
Predators were identified if they: a) approached within 2 m of the nest on the day on which the nest was predated (Haff and Magrath, 2011) and were detected by the camera or directly seen by the observers; or b) there was no such visual evidence, but there were bite marks on the plasticine eggs. In general, bite marks of small mammals showed small incisions from their teeth or a thin layer of the egg gnawed off, whereas the beaks of the large predatory birds made wide, penetrating gouges into the artificial egg (Fig. 2). To understand the repeatability of the distinction between mammal and bird eggs, we conducted blind tests with five Guangxi University students, verbally telling them that some of the bite marks were made by gnawing rodents and others by gouging birds. We found that only 2 of 70 (2.9%) of their identifications were different than ours. If all the eggs disappeared at once without any pictures (three instances), we categorized the predator as a snake, reasoning that only such a predator might be able to remove so many eggs without tripping the infrared camera. If a nest was predated by the same species more than once, we only counted one predation event. However, in the analyses of classes of predators, we did count multiple predation events if the species of predator were different (but such predation events by multiple predators occurred for only two nests).
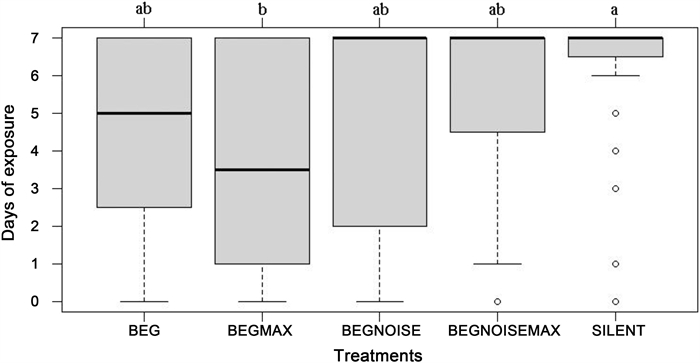
To understand how the treatments affected nest predation overall, we used the most detailed information available, the number of days the eggs in a nest were exposed and not predated. Because there was a maximum of seven days exposed, we expressed this number as a proportion of the maximum, and specifically, the response variable was a matrix, composed of the number of days the eggs were exposed without predation (D), and the number of days with predation (7-D). We then constructed a generalized linear mixed model (GLM) with a binomial distribution to understand the effect of playback treatment, year and the treatment: year interaction on this matrix, using the R statistical environment (R Core Team, 2021), base code. Likelihood ratio tests demonstrated that year and the interaction were not significant additions to the model and the model was simplified to the single factor of playback. Results from the model were overdispersed, so we re-ran the model with a quasibinomial error structure, followed by Tukey HSD multiple comparisons, using R package "multcomp" (Hothorn et al., 2008). We then tested three planned contrasts corresponding to the first three hypotheses: 1) whether predation was greater for the playback treatments, or the control; 2) whether predation was greater for maximum amplitude or mean amplitude; and 3) whether predation was greater for playback without traffic noise, or with traffic noise.
For understanding which predator classes (birds, mammals or reptiles) predated nests (hypothesis 4), we used a simpler, frequency table-based approach, as GLM models did not converge. For each of the first three hypotheses we constructed a two-by-two table summarizing the number of nests predated or not predated by the predator class (with three classes being birds, mammals and reptiles), dependent on the characteristic of the playback (control vs treatment, amplitude, inclusion of traffic noise). We tested whether these tables showed evidence of differential response based on the characteristic of the playback with Fisher Exact Tests. We consider p-values < 0.05 significant.
Predation of nests ranged between 1/2 and 2/3 of all nests across the three years (Table 1). A total of 94 nests were predated. We identified the predator (or predators, as two nests had multiple events with different predators) that predated the nest 62 times; 46 nests had visual detections (mostly photographs, two observations by the observers), and 16 nests had no visual detection, but did have bite marks. Of the predation events caught by the cameras or people, only seven were outside of the playback period (i.e., between 6 p.m.–6 a.m.; we did not collect the bite-mark information in a way that we could be sure of the time of predation) (Table 2).
| Treatment | Predation rate (%) | |||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
| natural (n = 4) | artificial (n = 8) | artificial (n = 8) | artificial (n = 12) | |||
| Natural amplitude of begging calls (BEG) | 50 | 50 | 62.5 | 41.7 | ||
| Maximum amplitude of begging (BEGMAX) | 100 | 75 | 75.0 | 83.3 | ||
| Traffic mixed with begging calls, natural amplitude (BEGNOISE) | 25 | 50 | 50.0 | 83.3 | ||
| Traffic mixed with begging calls, maximum amplitude (BEGNOISEMAX) | 50 | 50 | 62.5 | 75.0 | ||
| SILENT | 25 | 37.5 | 37.5 | 50.0 | ||
| Total | 50 | 53 | 57.5 | 66.7 | ||
| Treatment | Mammals | Reptiles | Birds | ||||||||
| Photo | Bitemark | Total | Photo | Bitemark | Total | Photo | Bitemark | Total | |||
| BEG | 3 (Squirrels) | 3 | 6 | 2 (Snakeb, lizarde) | 1 | 3 | 6 (4 GRCO, 2 ICGM) | 1 | 7 | ||
| BEGMAX | 4 (Mice)a | 4 | 8 | 1 (Snakee) | 1 | 2 | 8 (6 GRCO, 1 ICGMc, 1 ABOW) | 0 | 8 | ||
| BEGNOISE | 1 (Squirrel) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 (7 GRCOd, 1 ICGM) | 3 | 12 | ||
| BEGNOISE-MAX | 1 (Mouse) | 0 | 1 | 1 (Snake) | 0 | 1 | 3 (2 GRCO, 1 ICGM) | 3 | 7 | ||
| SILENT | 2 (Mice) | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 (3 GRCO, 1 ICGM, 1 UNID) | 0 | 5 | ||
| Totals | 11 | 7 | 18 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 31 | 7 | 39 | ||
| Most of the predators were identified visually (primarily by the cameras, with two identifications by the observers). Bite marks were identified based on the following properties of the predated eggs: eggs with small incisions or gnawing were categorized as attacked by a mammal, those with deep gouges as attacked by a bird, and multiple eggs that disappeared without triggering the infrared camera were categorized as attacked by a reptile (see text for further detail). This list includes two nests that were attacked by multiple predators. Abbreviations for the birds: GRCO = Greater Coucal (Centropus sinensis); ICBM = Indochinese Green Magpie (Cissa hypoleuca); ABOW = Asian Barred Owlet (Glaucidium cuculoides). For reptiles, we identified one Asian Green Pit Viper (Protobothrops mucrosquamatus), one Chinese Green Tree Viper (Trimeresurus stejnegeri), and one Eastern Garden Lizard (Calotes versicolor). a All four of these mice observations were outside the playback period, from 6 p.m. to 6 a.m.. b One snake observation was outside the playback period. c One magpie observation was outside the playback period. d One coucal observation was outside the playback period. e These observations were made visually by the observers. | |||||||||||
In 2018, the predation of the natural, abandoned nests (10/20) was close to the predation of the artificial nests (21/40). Also, the detected predators were similar between natural and artificial nests in that year (Appendix Table S1). Therefore, we used the artificial nests in further work and pooled together the results from natural and artificial nests. Predation in the years of 2019 and 2020 was somewhat higher (63/100) than predation in 2018, but not significantly so (Fisher's Exact Test, two-tailed, P = 0.34).
The number of days the eggs in nests were exposed without predation was affected by playback treatment (Total deviance = 826.4, deviance associated with treatment = 64.5, p-value [using Chi-Square approach] = 0.0057). Eggs stayed unpredated longest in the silent treatment, and shortest in the BEGMAX treatment (Fig. 3). Multiple comparisons showed only these two treatments to be significantly different from each other (z = 3.26, p = 0.0098; although BEGMAX also tended to have quicker predation than BEGNOISEMAX, p = 0.072). Contrast 1 showed that predation was quicker for playback treatments, compared to the silent control (t = 2.38, p = 0.019). Contrast 2 showed that predation did not differ depending on volume (t = 0.02, p = 0.98). Contrast 3 showed that predation was quicker for treatments that did not have traffic noise (t = 2.21, p = 0.029).
Of the nine tests made to understand how different predator classes contributed to predation depending on the characteristics of the playback, only one was significant. Mammals came more to playbacks without traffic noise (14 predation events) than to those with traffic noise (two predation events; two-tailed Fisher's Exact Test, p = 0.0023; if four mammal depredation events at night are removed from this analysis, p = 0.030). In contrast, birds came to the traffic noise treatments as much (19 times) as to the other playback treatments (15 times).
The results of the first contrast, connected to our first hypothesis, indicated that the playback of begging increased visits of nest predators to nests in our study, relative to silence. Using artificial nests (including the use of artificial eggs and/or an artificial nest structure) has been found to give different results than natural nests in nest predation studies (Zanette, 2002; Thompson Ⅲ and Burhans, 2004), likely because the behavior of adults is lacking, either in attracting predators (Martin et al., 2000), or in warning their nestlings (Platzen and Magrath, 2004). Our use of artificial nests must therefore be considered a limitation of the study. Nonetheless, we emphasize that many of the predators that were attracted to the nests (e.g., coucals, magpies, snakes, squirrels, and mice) are typical nest predators of our region (see data from Thailand; Pierce and Pobprasert, 2013; and Khamcha et al., 2018; and from southern Yunnan, China; Li et al., 2019). That begging attracts nest predators has also been shown in natural nests through playback (Haff and Magrath, 2011), and by the addition of loudly-begging brood parasites (Ibáñez-Álamo et al., 2012a). Most studies of begging and nest predation have, however, involved only one or a few kinds of nest predators (e.g., Haff and Magrath, 2011). Our study thus provides a useful assessment of the role of begging in influencing nest predation where there is a diverse nest predator community. It should be remembered, however, that begging is just one of many cues that nest predators use to detect nests. For example, during the incubation stage, visual predators may find poorly concealed nests, and during the nestling phrase they may eavesdrop on parental activity (Martin et al., 2000), so that nest predation may be similar in the different stages (e.g., Pierce and Pobprasert, 2013); at all times other predators such as snakes may search for nests using other sensory modalities such as olfaction (Soanes et al., 2015).
We did not find support for out second hypothesis that greater volume would increase nest predator response (the second contrast was nonsignificant), while the third hypothesis, that traffic noise would reduce response, was supported (third contrast was significant). In interpreting these results, we must keep in mind the nature of the traffic noise, collected on a large highway, that we used in the experiment. The experiment was conducted in the buffer zone of a tropical forest in which human noise is common, but large highway noise is not, and therefore some responses could have been stimulated by an unfamiliar noise. In particular, BEGNOISEMAX was quite obviously human-associated noise, whereas BEGNOISE sounded to the human ear like wind. There was less, on average though not significantly, nest predation in the BEGNOISEMAX treatment compared to the BEGNOISE treatment, perhaps suggesting that loud traffic noise was treated by the nest predators as particularly abnormal and repulsive; for example, birds responded 12 times to BEGNOISE, but only 7 times to BEGNOISEMAX. It is possible, though speculative since these differences are not statistically significant, that this effect could explain why volume did not increase response. Also, although we found evidence that traffic noise reduced response, the mechanism that led to this result might be different than anticipated: we thought that traffic noise would degrade the signal in begging calls, but it might also have been simply repulsive (see further discussion of the small mammal result, below). In the future, an experimental design that included a control treatment of traffic noise and no begging would be useful to better understand the effect of this kind of noise.
Our fourth hypothesis was that the masking of begging by traffic noise would be ineffective for nest predators with high frequency hearing, with the implication that if nestlings increased their begging amplitude in noisy areas (as shown by Leonard and Horn, 2005), this could also increase their vulnerability to these kinds of nest predators. We designed the experiment to try to look for this effect: we used traffic noise at close ranges that includes high frequency (up to about 6 Hz) components; there is evidence that large birds, like the nest predators involved in this study, may have poorer hearing sensitivities between 5 and 8 kHz than do smaller passerine birds (Klump et al., 1986). However, we must acknowledge that we may have failed to produce the correct environment to really test this hypothesis. The masking effect fluctuated with how close the cars approached, and large birds do have the ability to hear in the range of frequencies included in Red-whiskered Bulbul begging (~4.5–7.5 kHz). Overall, the avian nest predators in this study appeared to be able to detect the playback sounds (32 responses in 128 trials with playback, 5 responses in 32 trials of silence). However, it should also be remembered that birds, which are more likely to approach nests from above the ground, also had visual cues of nests, as they would be able to see the eggs in the nests.
We did find a difference in response to the treatments between predator classes, but not as expected: mammals predated fewer nests in treatments with traffic noise (14 responses without traffic noise, 2 responses with it). While the way in which we conducted this analysis followed our hypotheses in comparing broad classes of nest predators – mammals compared to birds and reptiles – it should be noted that in so doing we pool together two quite different kinds of mammalian nest predators: squirrels, which are diurnal, and mice, which may be primarily nocturnal (i.e., four of our seven photographs of mice were nocturnal with a further one crepuscular, within an hour of sunrise; other regional studies have found mice predation to be nocturnal; Pierce and Pobprasert, 2013; Li et al., 2019). It is possible that the lack of visits of mice to playback of traffic noise at night could be attributed to the animals moving away from the area when hearing the human-associated or unfamiliar noise in the area of the nests during the daytime. Alternatively, however, mice could be finding nests through olfaction, without the visual signal of the eggs, since they would be presumably approaching from the ground. Given that we had roughly equal numbers of mice (seven photographs) and squirrels (four) neither taken as a group themselves would have shown a significant avoidance of traffic noise.
That mammals in particular might be repulsed by human presence (termed a "scarecrow effect" by Leighton et al., 2010), has been suggested in some studies (Miller and Hobbs, 2000; Ibáñez-Álamo and Soler, 2010) and meta-analyses (Ibáñez-Álamo et al., 2012b). Small mammals are also known to avoid roads (McGregor et al., 2008), and noise in particular may influence their foraging decisions (Bednarz, 2021). Another study completed in the same study area also showed much reduced nest predation in conjunction with human activity (specifically the photography of nests by ecotourists; Tan et al., 2022).
The possibility that small mammals generally, or squirrel and/or mice more specifically, avoided treatments with noise is reminiscent of a growing body of work on how noise pollution can shift the composition of communities and species interactions. In a study of the effects of noise from industrial machinery, Francis et al. (2009) found that an avian nest predator was adversely affected by the noise, with cascading effects on the populations of birds it predated. This is apparently caused by the nest predator being less common in noisy areas. Further behavioral observations on how different classes of nest predators respond to noise is clearly warranted to understand the full conservation implications of human-produced noise (Francis and Barber, 2013). In particular, it would be useful to study these phenomena in a more urban environment where nest predators like rats or squirrels accustomed to human-dominated habitats are less likely to be repulsed by traffic noise.
SL, QX, AJ and EG developed the idea and wrote the first draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
This research was approved by the Nonggang National Nature Reserve, by the Guangxi University Animal Ethics Committee (GXU 2018-043), and followed the laws of the country in which it was conducted (People's Republic of China). We followed the Guidelines to the Use of Wild Birds in Research (Fair et al., 2010), particularly in the selection of an abundant species on which to work, and a small number of individuals involved (audio recordings of six nests, video recordings of three nests). In recording the nestlings, we took pains to not disturb them long-term (10 min per nest per visit, two visits); videorecorded nests were only visited to install and pick up the equipment. In the playback trials, the predators were rarely attracted to the nest a second time, and did not appear to digest the plasticine eggs; therefore, we believe their fitness was minimally affected.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
We thank Wenzhang Dai, Jiale He, Shuaiquan Qi, Xiaocai Tan, and Xiaolei Zeng for their assistance in the field. We appreciate the insightful comments of two anonymous reviewers that helped improve the manuscript. We are grateful to the villagers in Nonggang, who helped in the search for bird nests and were continually supportive. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 31870370) and Guangxi 1000 Young and Middle-Aged College and University Backbone Teachers Cultivation Program (2019.5).
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avrs.2022.100044.
|
Bednarz, P.A., 2021. Do decibels matter? A review of effects of traffic noise on terrestrial small mammals and bats. Pol. J. Ecol. 68, 323-333.
|
|
Fair, J., Paul, E., Jones, J., 2010. Guidelines to the Use of Wild Birds in Research. Ornithological Council, Washington D.C.
|
|
Ibáñez-Álamo, J.D., Magrath, R.D., Oteyza, J.C., Chalfoun, A.D., Haff, T.M., Schmidt, K.A., et al., 2015. Nest predation research: recent findings and future perspectives. J. Ornithol. 156, S247-S262.
|
|
Jiang, D., Nong, Z., Jiang, A., Luo, X., 2015. Breeding ecology and nest site selection of Red-whiskered Bulbul (Pycnonotus jocosus) in limestone area, northern tropical region of China. Chin. J. Zool. 50, 359-365.
|
|
Jiang, D., Zhou, F., Chen, T., Jiang, A., 2013. Breeding notes on 18 bird species in limestone area of southwestern Guangxi. Chin. J. Zool. 48, 597-604.
|
|
McGregor, R.L., Bender, D.J., Fahrig, L., 2008. Do small mammals avoid roads because of the traffic? J. Appl. Ecol. 45, 117-123.
|
|
Portfors, C.V., 2007. Types and functions of ultrasonic vocalizations in laboratory rats and mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 46, 28-34.
|
|
Ricklefs, R.E., 1969. An Analysis of Nesting Mortality in Birds. Smithsonian Institute Press, Washington, DC.
|
|
Slabbekoorn, H., Peet, M., 2003. Birds sing at a higher pitch in urban noise. Nature 424, 267, 267.
|
|
Stutchbury, B.J., Morton, E.S., 2001. Behavioral Ecology of Tropical Birds. Academic Press, London.
|
| Treatment | Predation rate (%) | |||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
| natural (n = 4) | artificial (n = 8) | artificial (n = 8) | artificial (n = 12) | |||
| Natural amplitude of begging calls (BEG) | 50 | 50 | 62.5 | 41.7 | ||
| Maximum amplitude of begging (BEGMAX) | 100 | 75 | 75.0 | 83.3 | ||
| Traffic mixed with begging calls, natural amplitude (BEGNOISE) | 25 | 50 | 50.0 | 83.3 | ||
| Traffic mixed with begging calls, maximum amplitude (BEGNOISEMAX) | 50 | 50 | 62.5 | 75.0 | ||
| SILENT | 25 | 37.5 | 37.5 | 50.0 | ||
| Total | 50 | 53 | 57.5 | 66.7 | ||
| Treatment | Mammals | Reptiles | Birds | ||||||||
| Photo | Bitemark | Total | Photo | Bitemark | Total | Photo | Bitemark | Total | |||
| BEG | 3 (Squirrels) | 3 | 6 | 2 (Snakeb, lizarde) | 1 | 3 | 6 (4 GRCO, 2 ICGM) | 1 | 7 | ||
| BEGMAX | 4 (Mice)a | 4 | 8 | 1 (Snakee) | 1 | 2 | 8 (6 GRCO, 1 ICGMc, 1 ABOW) | 0 | 8 | ||
| BEGNOISE | 1 (Squirrel) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 (7 GRCOd, 1 ICGM) | 3 | 12 | ||
| BEGNOISE-MAX | 1 (Mouse) | 0 | 1 | 1 (Snake) | 0 | 1 | 3 (2 GRCO, 1 ICGM) | 3 | 7 | ||
| SILENT | 2 (Mice) | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 (3 GRCO, 1 ICGM, 1 UNID) | 0 | 5 | ||
| Totals | 11 | 7 | 18 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 31 | 7 | 39 | ||
| Most of the predators were identified visually (primarily by the cameras, with two identifications by the observers). Bite marks were identified based on the following properties of the predated eggs: eggs with small incisions or gnawing were categorized as attacked by a mammal, those with deep gouges as attacked by a bird, and multiple eggs that disappeared without triggering the infrared camera were categorized as attacked by a reptile (see text for further detail). This list includes two nests that were attacked by multiple predators. Abbreviations for the birds: GRCO = Greater Coucal (Centropus sinensis); ICBM = Indochinese Green Magpie (Cissa hypoleuca); ABOW = Asian Barred Owlet (Glaucidium cuculoides). For reptiles, we identified one Asian Green Pit Viper (Protobothrops mucrosquamatus), one Chinese Green Tree Viper (Trimeresurus stejnegeri), and one Eastern Garden Lizard (Calotes versicolor). a All four of these mice observations were outside the playback period, from 6 p.m. to 6 a.m.. b One snake observation was outside the playback period. c One magpie observation was outside the playback period. d One coucal observation was outside the playback period. e These observations were made visually by the observers. | |||||||||||