| Citation: | Xiaoke Niu, Zhenyang Jiang, Yanyan Peng, Shuman Huang, Zhizhong Wang, Li Shi. 2022: Visual cognition of birds and its underlying neural mechanism: A review. Avian Research, 13(1): 100023. DOI: 10.1016/j.avrs.2022.100023 |
Birds have acute vision and many remarkable visual cognition abilities, due to their unique living environment. The underlying neural mechanisms have also attracted interests of researchers in neuroscience. Here, we firstly summarize the visual cognition abilities of birds, and make a comparison with mammals. Secondly, the underlying neural mechanisms are presented, including histological structure of avian brain and visual pathways, typical experimental results and conclusions in electrochemistry and electrophysiology. The latter mainly focuses on several higher brain areas related to visual cognition, including mesopallium ventrolaterale, entopallium, visual Wulst, and nidopallium caudolaterale. Finally, we make a conclusion and provide a suggestion about future studies on revealing the neural mechanisms of avian visual cognition. This review presents a detailed understanding of avian visual cognition and would be helpful in ornithology studies in the field of cognitive neuroscience.
Avian species have developed highly sensitive visual systems adapted to their living environment after more than a hundred million years of evolution (Herrnstein and Loveland, 1964). Compared with mammals, they are better at tracking small objects moving at high speed, and at identifying targets under low contrast and luminance conditions. For example, raptors flying thousands of meters in the air can easily detect prey moving rapidly on the ground (Fernandez-Juricic, 2012), and small birds are able to find hidden fruit and camouflaged insects in complex jungle environments (Vorobyev, 2003). Seagulls in the air can determine the location of swimming fishes in the water (Frost, 2009). Owls have excellent night vision and can move freely at night (Rowe, 2016). According to statistics, there are more than 10, 000 different species of birds with their unique habitats in the world (Hackett et al., 2008), and the different environments have also affected the evolution of the avian visual system (Daniel et al., 2015a, b; Murphy et al., 2015; Qadri and Cook, 2015). Even so, it is a general fact that the volume of bird eyes usually accounts for half or more of the cranial cavity, while mammals' eyes only account for less than 5%, suggesting there is more superior vision in avian species compared to mammals (including humans; Burton, 2008).
Birds have also developed remarkable and intelligent visual cognitive skills (Wright and Cumming, 1971; Zentall et al., 1986), even comparable to primates, especially for parrots and corvids, which have genomic similarities with humans (Wirthlin et al., 2018) and higher relative brain size (Ksepka et al., 2020). Recently, Nieder et al. (2020) found that the avian species displayed extremely high-level cognition, despite their pallium was organized in a very different way from mammals. For example, crows are reported to be able to distinguish paintings by Picasso and Monet (Anderson et al., 2020b), and pigeons can recognize cancer images (Levenson et al., 2015). Moreover, in daily life, gulls and kingfishers can easily locate their prey in water and dive from the air to the water to catch them. The remarkable visual cognitive abilities have attracted an increasing number of researchers devoted to revealing the underlying neural mechanisms; however, recent studies have been extensively conducted on mammals. Because of the extreme difference between organizational structures of avian and mammalian brains (Stacho et al., 2020), it could be speculated that birds might adopt different efficient neural encoding mechanisms to accomplish visual cognition (Güntürkün and Bugnyar, 2016). Studies on avian vision or visual cognition compared with mammals can help to understand the evolutionary history of birds. In addition, revealing the underlying neural encoding mechanisms may also help us to make clear how birds performed excellent visual cognition without a layered cerebral cortex (Nieder et al., 2020).
This review begins with a summary of the typical performance of visual cognition presented in birds. Previously reported conclusions about the neural mechanisms underlying avian visual cognition are then presented regarding the following three aspects: the histological structure of the avian brain and its main visual pathways, the neurobiological findings, and the electrophysiological results. Finally, some future research directions are suggested.
There has been a widespread bias regarding the level of visual cognition of birds. Albeit the connectivity of the avian brain conforms to the same organizational principles as the mammalian brain (Shanahan et al., 2013), it consists distinctively of nuclear and lacks a layered cerebral cortex (Dugas-Ford and Ragsdale, 2015; Karten, 2015; Olkowicz et al., 2016). The apparent anatomical dissimilarities have led to the misconception that birds may be inferior to mammals in cognition (Koenen et al., 2016). Nevertheless, a recent study by Nieder et al. (2020) showed that crows were able to perform subsequent actions based on their judgment of the brightness of the current visual cue, to receive a food reward, suggesting that birds were smarter than we previously thought. By training them to conduct a variety of behavioral experiments, zoologists have also verified that birds perform remarkably well in many complex visual cognitive tasks, as follows.
Studies have shown that some birds (typically crows, as well as songbirds) can grasp some simple cognitive rules (Wright and Delius, 2005). For example, birds are able to learn to decide what to do next according to the visual cues they saw previously in an associative matching task (Colombo, 2017), including a test of selecting the same or different item from the visual cues presented previously, and a test of performing or not performing specific actions.
Further cognitive testing studies have shown that birds are flexible in their learning of rules (Veit and Nieder, 2013). Roberts et al. (2016) trained pigeons to peck horizontal or vertical stripes for food rewards, with one of the options elected to reinforce their choice. After they got the rules, the reinforced option was then reversed. That is, pecking horizontal stripes previously would be provided food rewards, and in the reverse phrase, pecking vertical stripes would get food rewards. The results showed that pigeons quickly learned the new rules, suggesting pigeons' capacity of learning and flexible adapting to new rules. Similarly, female budgies can flexibly change the rules of mate selection, from the initial preference for males, to a preference for the ones who were able to solve extractive foraging problems (Chen et al., 2019). Additionally, a study by Zhao et al. (2019) verified the same cognition ability by training pigeons to perform a spatial goal-oriented task. The location of the target was changed repeatedly during the training process, and the pigeons quickly found the new location of the target by using a new different path.
The performance of birds in the rule reversal test and the ability to plan new paths in spatial navigation tasks both reflect the strong capability of birds to learn rules and flexibly adapt to new rules. This is a key for the survival and reproduction of birds in various complex natural environments.
Inference refers to the ability to think based on incomplete external information in order to solve a specified problem. Simple inference is one of the abilities necessary for animals to survive in a complex natural environment, and birds are no exception.
Transitive inference (TI) learning paradigm is always used to test animals' capability of inference, aiming to train animals to establish relationships between two or more unrelated items. It is always more difficult than immediate inference (ranking items directly related to each other), and has abundantly carried on primates (Guez et al., 2013). Recent studies showed that only some species of crows have TI learning ability. For example, crows were reported to be able to identify the priority of paper cups marked with different letters (Manns and Romling, 2012). Similarly, jackdaws can distinguish the rank order of five different colored squares (Mikolasch et al., 2013). Pinyon Jays (Gymnorhinus cyanocephalus) were trained to achieve high accuracy in list-linking tasks (Wei et al., 2014). In addition, the crow can rank autonomously according to the inherent physical characteristics of the target, such as the diameter of the circle (Lazareva et al., 2004). Although TI learning is a little harder than immediate inference, a few avian species are still capable of the task. Nevertheless, primates (such as macaques), are generally good at TI learning tasks (Clayton and Emery, 2015). TI learning has therefore been considered as an important reference for evaluating the cognition gap between birds and mammals (Emery, 2005).
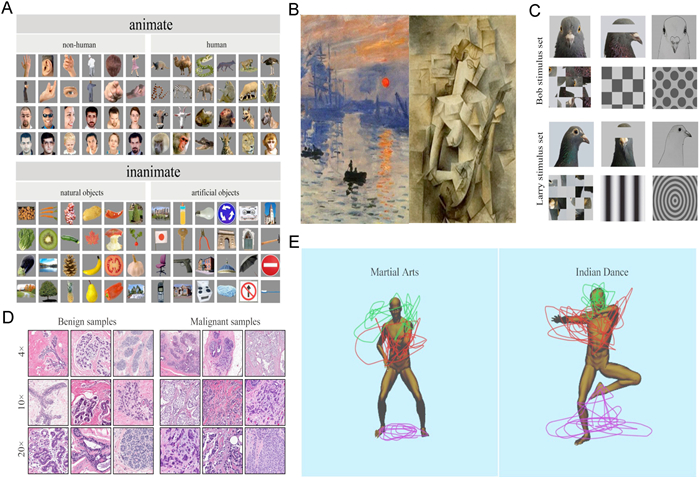
Object categorization task is the most widely used training paradigm to test visual cognition of animals. The core of object categorization is to capture key visual features among different objects and then perform corresponding actions according to the learned rules. Researchers have verified the remarkable ability of birds for object categorization, such as distinguishing human from nonhuman objects, identifying natural objects from artifacts (Fig. 1A; Watanabe, 1991; Azizi et al., 2019), recognizing different painting styles they did not see previously (Picasso versus Monet; Fig. 1B; Anderson et al., 2020b), discriminating a pigeon's facial pictures regardless of the direction of orientation or whether it is masked (Fig. 1C; Clark et al., 2019), distinguishing benign human breast histopathology images from malignant ones (Fig. 1D; Levenson et al., 2015), categorizing complex human behaviors (Verhaal et al., 2012), and distinguishing martial arts from Indian dances in both static pictures and videoes (Fig. 1E; Qadri and Cook, 2017). In addition, several studies on chickens and pigeons (Strockens et al., 2013) showed that the birds had a significant left-brain advantage in the visual target recognition, and that they preferred to identify objects from the right side of the visual field.
Sequence/structure learning is slightly different from target classification, and requires birds to extract and summarize sequence information contained in several targets. Compared with target classification, sequence learning tasks are more abstract. Animals must think at a deeper level and establish an abstract cognition of the sequence structure, rather than just finding differences among targets in a classification task.
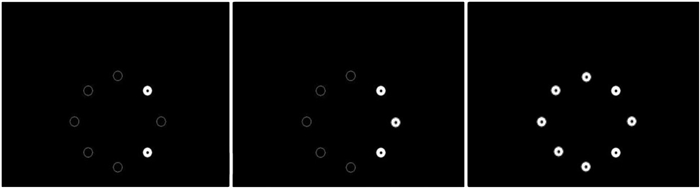
Due to the high level of abstraction, the testing paradigm of sequence/structure learning is more difficult to design. Serial multiple-choice tests are often used as paradigms, requiring animals to select targets according to a certain sequence. Garlick et al. (2017) found that pigeons performed best when there were four or five elements in the sequence. Either more or less would reduce the behavioral accuracy of the pigeon (Fig. 2). However, a few studies are testing the sequence structure learning ability of birds, and it is unclear how diversely different birds perform in sequence/structure learning. Furthermore, sequence structure learning has always been associated with numerical cognition, which has been widely conducted on crows (Corvus corone), and is an important representation of higher cognition (Ditz and Nieder, 2015; Nieder, 2020).
Invariant object recognition is another important visual cognition of animals. The performance of birds in invariant object recognition includes the following two aspects.
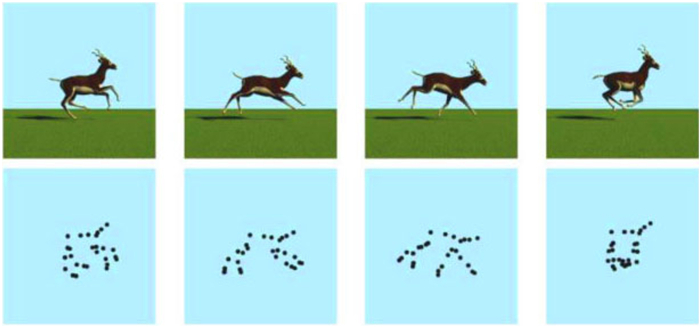
Birds are able to recognize and classify a specified object by grasping its contour information, even with very little information. A typical study, conducted on pigeons (Cook et al., 2015), showed that they could correlate photographs of real animals in motion with their sparsely dotted outlines (Fig. 3).
The ability to recognize an object using a small amount of contour information is a dimension-reduction perception ability evolved by birds for continuous adaptation to their living environments (Cook et al., 2013). The ability allows the birds to establish an abstract mapping of highly dimensional complete information through incomplete low-dimensional information. It is also an important representation of their higher cognition. Because birds are a species that often flies in the air, they may not be equipped to see detailed information of the target due to their high-flying speed and long visual distance, especially when preys are simultaneously running in different directions at high speed. The ability of contour-based invariant object recognition would therefore help birds to locate prey based on their rough outlines.
In the natural environment where birds live, the target is often partially masked by other items, making it difficult to recognize. However, this limitation does not baffle birds. A cognition test performed on parrots (Pepperberg and Nakayama, 2016) showed that they could classify circles, even partially obscured by other shapes. Another test on chicks (Wood and Wood, 2015) showed that the chicks could recognize three-dimensional objects with some visual angles that had never been seen before after they were trained using a few other view angles. The above studies suggest that birds have the ability to global perception of a specified object even it is spatially separated or in different visual angles (Cook et al., 2013; Peissig et al., 2005).
Studies have found that subjective cognition of the brain can affect the objective perception of the surrounding items to some extent. For example, the perception of humans to target size, line length, and area brightness may vary according to different references (Herbranson et al., 2017; Punsawad et al., 2021). This phenomenon, called visual perception illusion, is thought to occur only in mammals with highly developed cognition (Norton and Corbett, 2000; Coello et al., 2007; de Brouwer et al., 2015; Geers et al., 2018; de la Malla et al., 2019). However, behavioral tests performed on crows' cognition have recently found a similar phenomenon, the bird may make opposite judgments on the same object in the presence of different references (Rinnert and Nieder, 2021), indicating the subjective cognitive judgment of the bird surpasses the underlying objective information obtained by the primary sensory areas in the cognitive processing (Spetch and Friedman, 2006). This phenomenon also provides strong evidence that birds have advanced cognition. Birds can refer to the surrounding environment for subjective thinking and make judgments, rather than simply depend on objective environmental information to obtain the information (Nieder et al., 2020).
Birds have evolved a different pallium since they diverged from the mammalian lineage 320 million years ago (Kumar and Hedges, 1998; Hedges, 2002). Nevertheless, the bird pallium retains organizational principles reminiscent of the mammalian brain (Stacho et al., 2020). The structure is usually the basis of function, thus there could be more similarities than differences in neural mechanisms related to visual cognition between the two species. However, neuroscience studies have often focused on the brains of mammals, which are closer to humans than other vertebrates. There were much fewer studies revealing the neural mechanisms related to visual cognition of birds, compared to mammals. The following section reviews several typical conclusions about the neural mechanisms of visual cognition in birds, as compared with those of mammals.
The avian brain lacks a layered cerebral cortex, which exists only in mammals, but there are some structural homologies between the two species (Jarvis et al., 2014; Güntürkün and Bugnyar, 2016; Scarf et al., 2016a, b).
Globally, researchers found that the connectivity among both avian and mammalian brains presented small-world properties, suggesting the avian brains of birds may be structured in a similarly efficient way as mammals. Shanahan et al. (2013) constructed the first global "connection map" of the avian endbrain. The results of graph theory analyses on the connection graph showed that the avian endbrain had small-world properties, similar to that of mammals. The emerging hub nodes were the most core and closely-connected areas of the brain, suggesting that these nodes played a key role in information transmission and processing (Atoji and Wild, 2012).
Locally, Stacho et al. (2020) found that the primary brain regions in pigeons and owls had horizontal layered and vertical columnar structures, similar to the layered structure of the mammalian neocortex. Those studies provide the physiological basis for birds' ability to perform higher cognition functions. Taken together, birds and mammals have homologous brain structures both locally and globally.
In terms of retina structure, the bird is quite similar to other vertebrates, with the same types of cells and the same general structure. For example, the retina of both birds and mammals have rod cells and cone cells, the former of which is responsible for perceiving light and the latter is responsible for perceiving colors. Specifically, birds have four types of cone cells, while mammals and humans have only three. Thus, birds are sensitive to ultraviolet light besides red, green, and blue light, and can distinguish other non-spectral colors. The density of retinal cones in daytime birds is higher than nocturnal birds, whose retina is dominated by rod cells. And, unlike primates, which usually have only one fovea, most bird retinas have two fovea structures, one of which can improve visual acuity in the lateral field, and the other may increase visual acuity in the front field.
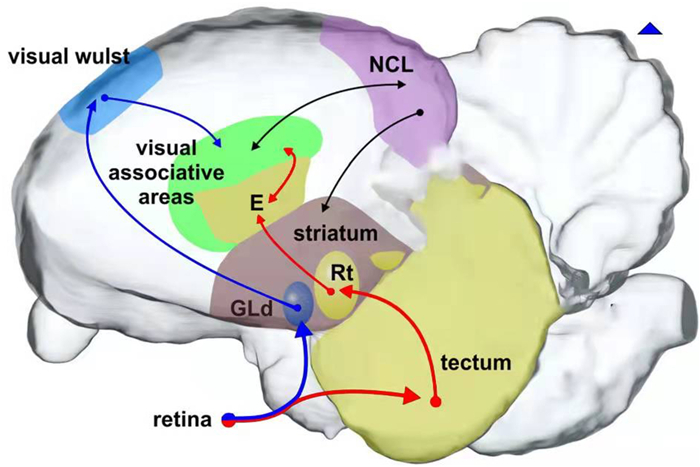
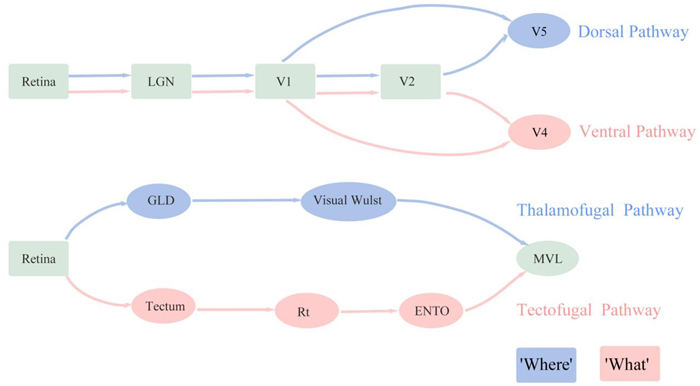
There are two main visual pathways in the avian brain, consistent with those in mammals, including tectofugal and thalamofugal pathways, corresponding to the "what" and "where" pathways in mammals (Stacho et al., 2016). The tectofugal pathway (Fig. 4, labeled with red arrows) receives visual information from the frontal visual field, which is transmitted from the retina to the optic tectum (OT), then to the rotundus (RT) and further to the entopallium (ENTO; Wang et al., 1993; Cook, 2000; Krutzfeldt and Wild, 2005). The pathway mainly focuses on object classification and is a key pathway used by birds to visually recognize objects. The thalamofugal pathway (Fig. 4, marked by blue arrows) mainly receives visual input from the lateral visual field, which is also transmitted from the retina, through the Gld (the nucleus geniculatus lateralis par dorsalis), and finally to the visual Wulst (Ng et al., 2010), focusing on processing motor information about the target. It is mainly responsible for answering "where the target is", and is the main pathway used by birds to track targets and to estimate their distance from the target. Except that the brain regions of the visual pathways in birds are not as finely divided as in mammals, another main difference of visual pathways between birds and mammals is that the two pathways of birds separated after the retina, while for mammals the visual input was processed by retina, lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), the primary visual cortex (V1) and V2 and then separated into two pathways (Fig. 5).
In addition, for birds, the left and right hemispheres of the tectofugal pathway present asymmetry, while those of the thalamofugal pathway show no significant differences (Strockens et al., 2013). This was consistent with the behavioral findings that chickens and pigeons exhibited left-brain dominance in visual target recognition (Strockens et al., 2013; Morandi-Raikova et al., 2021). Taken together, the results show the key role of the tectofugal pathway in visual target recognition (Koenen et al., 2016).
Furthermore, histological structural studies show that there are neural projections between the visual Wulst (the end of the thalamofugal pathway) and the mesopallium ventrolaterale (MVL), and between the ENTO (end of the tectofugal pathway) and MVL (Atoji and Wild, 2012), suggesting that output of the two pathways in the avian converges in the MVL. The interconnection of neurons among these related brain regions is the basis of distributed information processing in the brain. It can therefore be inferred that the global category information of the target (color, shape, etc.; Lombardi, 2007; Zentall et al., 2008), outputted from the tectofugal pathway, and their spatial information (the relative position, motion, speed, etc.), transmitted from the thalamofugal visual pathway, are further integrated into the MVL (Güntürkün et al., 2018). However, this conclusion needs further verification.
In addition to the above two main visual pathways, birds also evolved a special accessory visual pathway for their survival needs. It is mainly composed of the nucleus of the basal optic root (nBOR) and lentil nucleus, and is used to produce the oculomotor tremor reflex and stabilize the retinal image by compensating eye movements. Among them, the nBOR is homologous to the medial and lateral terminal nuclei in mammals (Wylie et al., 2008), and the homologous structure of the nucleus lentiformis mesencephalis (nLM) in mammalian is the nucleus of the optic tract (NOT) of the midbrain in avian species (Xiao and Frost, 2009; Stacho et al., 2016).
In addition to the above brain areas, the avian pallial endbrain area, nidopallium caudolaterale (NCL), is another important area used for processing higher cognitive functions. It shows many similarities to the mammalian prefrontal cortex (PFC) in connectivity, dopamine neurochemistry, and function (Güntürkün and Bugnyar, 2016; Güntürkün et al., 2021). Multi-sensory information is aggregated in the NCL for further processing, and then outputted to motor areas to generate corresponding behaviors (Güntürkün et al., 2018). Studies have shown that there are neural connections between the MVL and NCL (Shanahan et al., 2013), indicating that the MVL may send integrated category information of visual targets to the NCL for further processing.
Neuronal activity could be reflected by changes in levels of relevant neuromodulators (Berg and Grace, 2011). Several neuromodulators, including dopamine, 5-HT (5-hydroxytryptamine, commonly known as serotonin), and acetylcholine (ACh), achieve a dynamic balance through complex interaction mechanisms, which enables animals to perform learning and cognitive activities efficiently. Dopamine is essential for cognitive control functions of high-level brain area, e.g. PFC in mammals (Ott and Nieder, 2019) and NCL in birds (Güntürkün et al., 2018). During cognition, dopamine neuron activity (especially D1 receptor) is mainly related to reward error, which represents the "relative" reward value (Waelti et al., 2001). 5-HT neurons represent an "absolute" reward value and are widely distributed in the brain and mainly act in the forebrain. They are mainly excitatory in learning and memory activities, and can affect the maintenance of animal visual memory to a certain extent. ACh is distributed in the central cholinergic system, and closely related to learning and memory function (Hasselmo, 2006). The cholinergic system is activated when awake, freely moving animals need to analyze new stimuli or perform exploratory behavior in a new environment. Acetylcholine is always mediated by M2 and M4 receptors to inhibit the generation of high-frequency ripple rhythms in the hippocampus (usually related to the consolidation of memory) in the waking state of animals (Ma et al., 2020).
For birds, the current studies mainly focused on dopamine neuronal activity during visual cognition. Güntürkün et al. (2018) suggested that in birds, the amount of dopamine released in the NCL was related to partial dopamine neuronal activity, which varied during associative learning, in a similar manner as mammals. Blocking dopamine receptors in the pigeon endbrain eliminated differences between learning rates associated with different reward magnitudes, and also destroyed local visual attention (Knudsen, 2018; Krauzlis et al., 2018).
Increases/decreases of dopamine depend on changes between actual rewards and expectations (Schultz, 1998; Güntürkün et al., 2018; Ott and Nieder, 2019). When the actually given reward is less than expected, or the expected reward is not given, dopamine neurons of the pigeon brain reduce their activities until the expected given reward is given (Nomoto et al., 2010). When the given reward is larger than expected, dopamine neurons increase their response intensity (Bayer and Glimcher, 2005). When the rewards are consistent, the activity of dopamine neurons remains unchanged (Schultz, 2016).
The nervous system can correlate subjective values with objective events when it is mediated by dopamine (Gadagkar et al., 2016). When the obtained rewards are smaller than the birds expected, the dopamine neurons are inhibited, leading to a reduction of released dopamine, which further serves as a feedback signal acting on other related brain regions to affect some cognition functions, such as decision-making. As a result, the pigeon brain can change the behavioral strategy or expectation until the expected results are close to the actual payments (rewards).
Thus, dopamine-mediated, error-driven feedback learning mechanisms enable birds to selectively focus on the relevant stimulus features and pay more attention to the key features of the target during the visual target classification task (Fields et al., 1984; Campos et al., 2011; Castro and Wasserman, 2013; Soto and Wasserman, 2014; Vyazovska et al., 2014, 2016, 2021; Teng et al., 2015; Koenen et al., 2016; Ott and Nieder, 2019). The amount of released dopamine is quickly adjusted according to the reward expectation discrepancy, providing biological feedback for birds to quickly learn classification rules (Soto and Wasserman, 2011; Cook et al., 2013).
Microelectrode technique has become the main method to explore neuronal response properties of animals' brains. Because transgenic technology has not been widely implemented in birds, optical imaging techniques are limited in studying the neural mechanisms of birds' brains. In addition, there are much fewer studies (Van Meir et al., 2005; de Groof et al., 2013; Behroozi et al., 2017, 2020) using fMRI to explore the avian brain, relative to mammals. Thus, we mainly focused on the electrophysiological results of visual cognition.
The cognitive process of visual object recognition can usually be divided into two levels: visual perception and cognitive decision-making. The visual perception of a target is mainly completed by the primary stage of the visual pathway, which receives considerable redundant visual information. Thus, the main task of preliminary processing is to reduce visual redundancy and extract basic primary visual features, which are further transmitted to higher brain areas for further integration to generate invariant features, and then output decision signals to guide behaviors. Under natural environmental conditions, this process can be completed instantaneously by the brain. However, in order to study each process at each stage of the visual pathway, specific cognition training tasks need to be designed to decompose the whole cognition process. Delayed matching-to-sample (DMS) tasks are a classical visual behavioral cognitive training paradigm used to study different cognition processes (Olkowicz et al., 2016; Anderson et al., 2020a, b). In DMS paradigm (Fig. 6), tasks are divided into an observation period during visual object presentation (Daniel et al., 2015a, b), a delay period during visual cognition formation, and a decision-making period before outputting behavior, as well as the reward payment period occurring after performing an action (Azizi et al., 2019). A typical electrophysiological experimental paradigm used to study the neural mechanism of visual cognition was as follows. After implanting a single microelectrode or array in any brain region related to visual cognition, the birds are trained to perform a delayed matching task, and the neural data are simultaneously recorded (Ditz and Nieder, 2015, 2016; Moll and Nieder, 2015; Veit et al., 2017; Nieder, 2020). The response during each period is then characterized to build the relationship between neural response with cognitive activity and further determine the role of each brain region in visual cognition.
The electrophysiological properties of neurons in the primary sensory brain region have been widely reported (see a recent review (Clark and Colombo, 2020) for more information). Our review mainly focuses on describing neural mechanisms related to visual cognition. Thus, we mainly summarized the current studies on electrophysiological properties of neurons in several higher brain areas, including the ENTO, visual Wulst, MVL, and NCL (Yang et al., 2005; Johnston et al., 2017).
Scarf et al. (2016b) found that neurons in the ENTO responded strongly to multiple visual targets, and preferred a broad, overlapping type of stimulus. Anderson et al. (2020b) found that neurons in both the ENTO and visual Wulst in pigeons fired more intensely than baseline in both the visual presentation and delay periods, suggesting that neurons in both brain regions had flexible coding properties, encoding both stimulus target information and reward information.
The GO/NO-GO task is a variant of the DMS task (Wilkie et al., 1981; Marzluff et al., 2012), and is always used to characterize the role of the NCL, related to reward information, in cognition. In this task, the targets are always defined as S+ and S– (Cole et al., 2020), respectively. In the trial presenting S+, when the birds were trained to perform the corresponding action correctly (such as pecking the screen or keyboard), they would receive a food reward. In presenting S–, the birds did not receive a food reward. By establishing two possibilities of reward/no reward during the reward period, the reward information was introduced as one of the factors that should be considered when birds performed a behavior. It was found that the excitatory neurons in the NCL of pigeons responded intensely both in the target presentation and delay stages of cognition forming, while inhibitory neurons only fired during the latter period (Johnston et al., 2017). This suggested that neurons in the NCL encoded reward information related to visual targets, rather than the target information itself. Furthermore, Veit et al. (2017) reported that many single NCL neurons of crows were spatially tuned to specific target positions during visual searching, and dynamically changed their tuning properties to represent different behaviorally relevant task variables across the trials. Cognition tests on crows (Nieder, 2020) further showed that the response of NCL neurons during a detection task composed of two stages, the first of which mainly reflected physical stimulus intensity, whereas the latter predicted perceptual reports, suggesting that sensory consciousness may have arisen either before the emergence of mammals or independently in at least the avian lineage, which lacks a layered cerebral cortex.
Additionally, a study that implanted microelectrodes in three brain areas of pigeons simultaneously, including the MVL, ENTO, and NCL, found that those brain areas were responsible for different stages of visual information processing (Anderson et al., 2020b). The results showed that the MVL and ENTO shared stimulus-related information about the categories, and the NCL and ENTO shared reward information about the categories, indicating that the MVL, as a higher-order visual association region relative to the ENTO, may encode categorical information in a similar yet more complex manner than in ENTO.
The present review summarizes the developed visual cognitions of some avian species and the underlying neural mechanisms, including the histological structure of visual pathways, the experimental results, and conclusions in neurobiology and electrophysiology. The remarkable visual cognitive skills mainly focus on species such as the order Galliformes (chicken), Passeriformes (magpie, crow), and Psittaciformes (parrot); however, there are over 10, 000 species of birds, also suggesting a diversity of visual cognition abilities among birds. The histological results showed that although the nuclei-based avian brain is quite different from the layered cerebral cortex of the mammalian brain, visual pathway in both species have many similar structural characteristics, suggesting that the visual system of birds may have a similar efficient information processing mode (Shanahan et al., 2013). Neurobiological results performed on birds mainly focused on the role of dopamine in visual cognition. The electrophysiological results showed that the ENTO of the tectofugal pathway and the visual Wulst of the thalamofugal pathway were responsible for processing category and motion information of the target, respectively. In addition, the MVL integrates information from different pathways and sends it to the NCL for further processing to complete cognition computing and decision-making. The NCL shows high similarities with the PFC of mammals in both function and structure, and the response of neurons in the NCL is more related to reward information.
Taken together, histological structural studies are relatively advanced, while neurobiological and electrophysiological studies are less advanced, especially electrophysiological studies, which mainly focus on reporting the role and function of a single brain region in performing a certain cognition task. It is well known that any visual cognition task of the brain (whether it is an auditory, visual, or other tasks) requires the cooperation of neurons in multiple brain regions. Research on cooperative information processing among multiple brain regions has been mainly conducted in mammals (such as monkeys, rats, and mice; Liu et al., 2021; Xue et al., 2021). Only fewer studies (Hsiao et al., 2020) revealed the cooperative mechanisms among multiple brain regions in birds while performing specific cognition tasks. For example, Hsiao et al. (2020) found that the information interaction between the ENTO and the NCL was significantly stronger than that between the visual Wulst and the NCL of Zebra Finches (Taeniopygia guttata) when identifying different colors, suggesting that color information was transmitted through tectofugal pathway to the NCL. In addition, Zhao et al. (2019) studied how the hippocampus (responsible for forming memory) was coupled with the NCL (responsible for forming cognition) during goal-oriented path planning tasks and Cheng et al. (2020) further found that the functional connectivity between the hippocampus and NCL were significantly increased. Further studies showed that the direction of information flow was from the hippocampus to the NCL.
In conclusion, electrophysiological studies on neural mechanisms related to visual cognition in birds are still in the preliminary stages. At present, the general functions of several higher brain regions have been reported. However, which brain region is responsible for processing more sophisticated visual cognition activities is not yet known. The visual target cognition tasks conducted on birds mostly use different colors as visual cues, but rarely use shape or contour information as cues, due to their preference for color information. However, shape and color are both important features of visual objects. Whether there are similarities or differences between the strategies of encoding color and shape by higher brain regions of birds is not known. Second, whether there is a special brain area responsible for processing invariant target recognition, like inferior temporal in mammals remains unknown (Tanaka, 1996; Cook, 2000; Sigala and Logothetis, 2002; Srihasam et al., 2014). Behavioral studies have shown that chickens can achieve invariant three-dimensional shape recognition (Wood and Wood, 2015), but there is a lack of experimental histological or electrophysiological validation. In addition, some bird species are comparable to mammals in terms of visual cognition. Therefore, it is of great significance for future studies to characterize the information interaction between multiple brain regions during different periods of visual cognition tasks. These studies will help to explain how those birds have evolved a unique brain with its structure different from mammals but with comparable intelligence, or at least not inferior to.
XN: conceptualization, funding acquisition, original draft, review and editing; ZJ: conceptualization, original draft, review and editing; YP: review and editing; SH: review and editing; ZW: project administration, review and editing; LS: supervision, review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61673353), and the Key Scientific Research Projects of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province, China (No. 20A413009). We thank International Science Editing (http://www.internationalscienceediting.com) for editing this manuscript.
|
Behroozi, M., Helluy, X., Strockens, F., Gao, M., Pusch, R., Tabrik, S., et al., 2020. Event-related functional MRI of awake behaving pigeons at 7T. Nat. Commun. 18, 4715.
|
|
Cheng, S., Li, M., Yu, H., Zhao, K., Liu, S., Wan, H., 2020. Decoding pigeon behavior outcomes during goal-directed decision task by WSR functional network analysis. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 38-41.
|
|
Daniel, T.A., Cook, R.G., Katz, J.S., 2015. Temporal dynamics of task switching and abstract-concept learning in pigeons. Front. Psychol. 6, 1334.
|
|
Emery, N.J., 2005. Cognitive ornithology: the evolution of avian intelligence. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 361, 23-43.
|
|
Gunturkun, O., von Eugen, K., Packheiser, J., Pusch, R., 2021. Avian pallial circuits and cognition: a comparison to mammals. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 71, 29-36.
|
|
Ksepka, D.T., Balanoff, A.M., Smith, N.A., Bever, G.S., Bhullar, B.S., Bourdon, E., et al., 2020. Tempo and pattern of avian brain size evolution. Curr. Biol. 30, e2023.
|
|
Shanahan, M., Bingman, V.P., Shimizu, T., Wild, M., Gunturkun, O., 2013. Large-scale network organization in the avian forebrain: a connectivity matrix and theoretical analysis. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 7, 89.
|
|
Soto, F.A., Wasserman, E.A., 2014. Mechanisms of object recognition: what we have learned from pigeons. Front. Neural Circuits 8, 122.
|
|
Stacho, M., Herold, C., Rook, N., Wagner, H., Axer, M., Amunts, K., et al., 2020. A cortex-like canonical circuit in the avian forebrain. Science 369, 6511.
|
|
Veit, L., Hartmann, K., Nieder, A., 2017. Spatially tuned neurons in corvid nidopallium caudolaterale signal target position during visual search. Cereb. Cortex 27, 1103-1112.
|
|
Wood, S.M., Wood, J.N., 2015. A chicken model for studying the emergence of invariant object recognition. Front. Neural Circuits 9, 7.
|